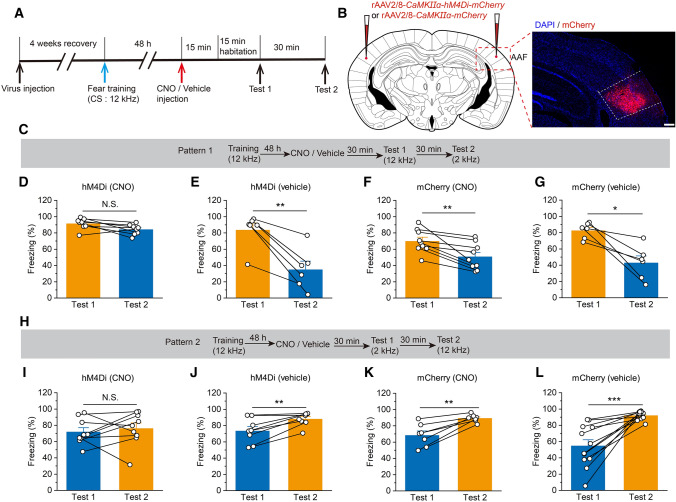
Fig. 4.
Significant reduction in auditory frequency discrimination due to pharmacogenetic inhibition of AAF pyramidal neurons. A Experimental timeline for virus injection and behavior testing. B Schematic showing bilateral injection of virus into the AAF. Scale bar, 200 μm. C Experimental scheme for the training and fear conditioning test of pattern 1. D Pharmacogenetic inhibition of hM4Di+ pyramidal neurons in the AAF (injected with CNO) significantly disrupts the auditory frequency discrimination behavior (n = 8). E Vehicle injection does not influence the auditory frequency discrimination behavior of hM4Di-infected animals (n = 6). F, G The mCherry-infected mice (injected with CNO or vehicle) significantly differentiate the two frequency tones (F: n = 9; G: n = 6). H Experimental scheme for the training and fear conditioning test of pattern 2. I Pharmacogenetic inhibition of pyramidal neurons expressed hM4Di (injected with CNO) significantly disrupts the auditory frequency discrimination behavior (n = 9). J Vehicle injection does not influence the auditory frequency discrimination behavior of hM4Di-infected animals (n = 8). K, L The mCherry-infected mice (injected with CNO or vehicle) significantly discriminate the two frequency tones (K: n = 7; L: n = 12). All data are shown as the mean ± SEM, N.S., no significant difference; **P <0.01, ***P <0.001, paired Student’s t-test.