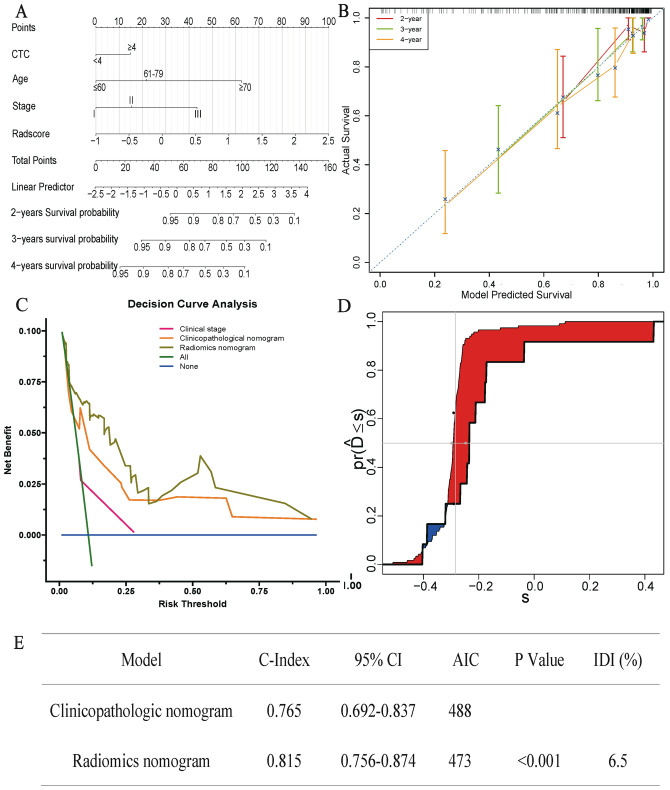
Fig. 2.
Comparison of prognostic prediction performance between radiomic nomogram and clinicopathological nomogram. A. The radiomics nomogram constructed using the training data set was used to predict the prognostic risk of patients with “driver gene-negative” LUAD. B. The calibration curves demonstrated that the radiomics nomogram had a good prediction performance of the survival probability at 2, 3 and 4 years after diagnosis. C. The decision curve showed that radiomics nomogram (solid brown line) was a model with a higher net income than clinicopathological nomogram (solid orange line) under most of the given thresholds. D. The integrated discrimination index (IDI) indicated that the prediction performance of radiomics nomogram model was 6.5% higher than that of clinicopathological nomogram model. E. The estimated concordance index (C-index) and Akaike information criteria (AIC) of the radiomic nomogram and clinicopathological nomogram