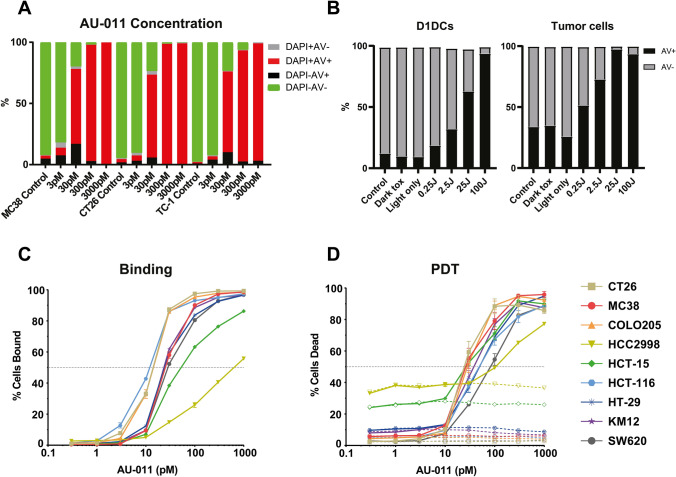
Fig. 2.
AU-011 treatment with light activation preferentially induces cytotoxicity in cancer cells over APCs. A MC38, CT26 or TC-1 were incubated with 3–3000 pM of AU-011 in the dark for 4 h. Cells were then illuminated with NIR light (690 nm) light at 400 mW/cm2 for 25 J/cm2. At 18 h after treatment, the samples were stained with viability markers Annexin V-FITC and DAPI before analysis by flow cytometry. Representative graph of ≥ 3 independent experiments. B A co-culture containing an equal number of MC38CFP and D1DCs were incubated with 300 pM of AU-011 in the dark for 4 h. Cells were left in the dark (dark toxicity, dT), treated with NIR light only at 400 mW/cm2 for 100 J/cm2 (light only), treated with AU-011 with light activation by illumination with NIR at 400 mW/cm2 for 0.25–100 J/cm2 or not treated with either AU-011 or light (control). At 18 h after treatment, the samples were stained with CD11c-PE and viability marker Annexin V-FITC before analysis by flow cytometry. Separation of MC38CFP and D1DCs was based on CFP+ (cancer cells) or CD11c+ (immune cells), showing (left panel) D1DCs and (right panel) tumor cells. A panel of colon cancer cell lines was tested for C percentage of cells bound to AU-011 and D cytotoxicity of AU-011 PDT at various concentrations of PS, comparing dark toxicity (dotted lines) with PDT treatment at 25 J/cm.2 (solid lines). (mean ± SEM; n = 3)