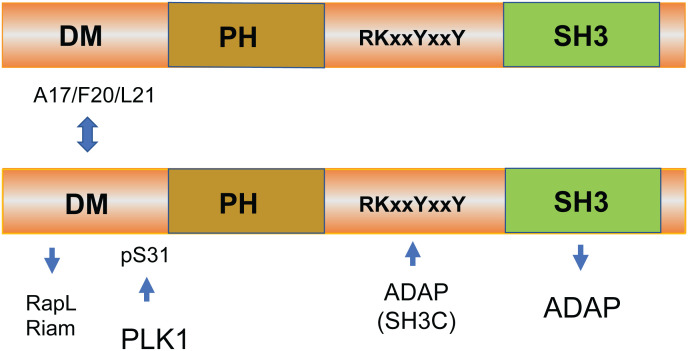
Figure 1.
The structure and binding sites of SKAP1. Human SKAP1 possesses an N-terminal dimerization (DM) domain, a species-specific disordered region, a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain (N107–K210), and a C-terminal SH3 domain (D294–E355) (33, 39). SKAP1 binds to ADAP via its SH3 domain and, to a lesser extent, via a SKAP1 RKxxYxxY motif that binds to an SH3C domain (41, 42). SKAP1 can form homodimers or heterodimers with related SKAP2 (SKAP-related R or SKAP-Hom) in cells mediated by residues A17 to L21 in the SKAP1 N-terminal region (43). The function of dimer formation is not known.