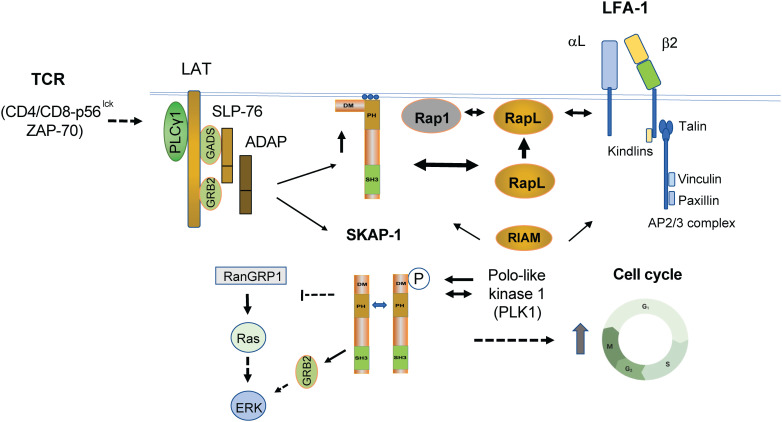
Figure 2.
TCR induced pathways linking SKAP1 to the regulation of integrin-mediated adhesion and intracellular proliferation pathways. TCR ligation leads to the formation of the LAT signalosome (LAT and associated SLP-76, GADs, ADAP, and SKAP1). TCR (and CD28) also induces the presence of D-3 lipids, which bind and recruit SKAP1 via its PH (pleckstrin homology) domain to the plasma membrane (PM). By binding to RapL in the cytoplasm, SKAP1 acts as a chaperone or shuttle protein to transport RapL to the PM to interact with the GTP-binding protein Rap1 (see upper heavy arrow between SKAP1 and RapL where RapL is moved to the cell surface upward heavy arrow). The RapL–Rap1 complex depends on the presence of SKAP1 as shown by the observation that complex formation fails to form in skap1-/- primary T cells in response to TCR ligation. The complex at the cell surface with associated SKAP1 then binds to the αL chain of LFA-1. Concurrently, SKAP1 also binds to RIAM via the DM domain. By contrast to the αL chain, the β2 chain binds to Talin and various Kindlins in a complex that includes direct Talin binding to RIAM, Paxillin, and Vinculin (see upper right image of LFA-1). Complex formation promotes increased affinity as well as the clustering of LFA-1 for increased binding avidity in binding to ICAMs. SKAP1 also forms a dimer via its DM domain where it regulates the movement of SLP-76 micro-clusters. Whether dimerization controls the binding of RapL and RIAM is not known. In addition to mediating integrin activation, SKAP1 is phosphorylated by and binds to Polo-like kinase (PLK1) for the optimal cycling of T cells (see lower image of SKAP1 dimer). PLK1 binds to the N-terminal residue serine 31 (S31) of SKAP1 and the interaction is needed for optimal PLK1 kinase activity and cell cycling. The C-terminus of SKAP1 also binds to RasGRP1 and can negatively regulate the p21ras-ERK pathway or in binding to GRB-2 may promote ERK activation. Whether this occurs alone or in conjunction with GRB-2 binding to LAT remains to be resolved. Solid arrows indicate direct interaction, whereas dotted arrows reflect indirect and unestablished interactions.