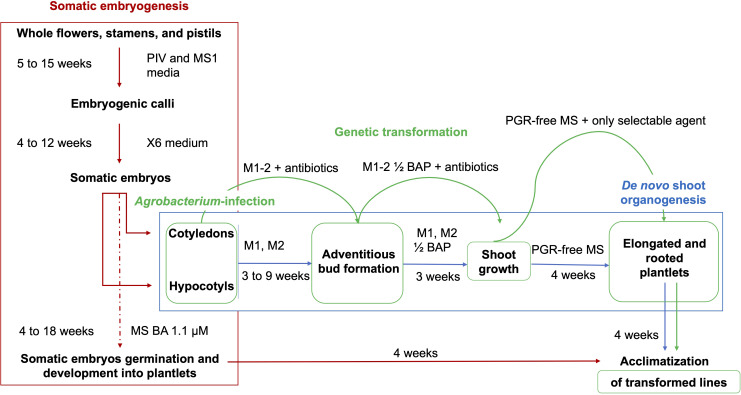
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of the regeneration methods and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation protocols from cotyledons and hypocotyls obtained from flower-derived somatic embryos of grapevine cultivars. Embryogenic calli are obtained from the culture of whole flowers, stamens, and pistils on PIV and MS1 media. These calli are continuously proliferated on X6 medium, with the production of somatic embryos at the cotyledonary stage. The somatic embryogenesis regeneration pathway is interrupted through the isolation of cotyledons and hypocotyls from the somatic embryos, which are separated and induced to form adventitious shoots on appropriate regeneration media (M1 and M2). Shoot development occurs in media with halved BAP concentrations, while the elongation and the emergence of roots are stimulated from the shoots in a PGR-free MS medium, which is followed by the acclimatization in the greenhouse. Agro-infected cotyledons and hypocotyls chase the same steps for the stimulation of de novo shoot formation, in media supplemented with 420 µM cefotaxime, 475 µM carbenicillin, and 146 µM kanamycin.