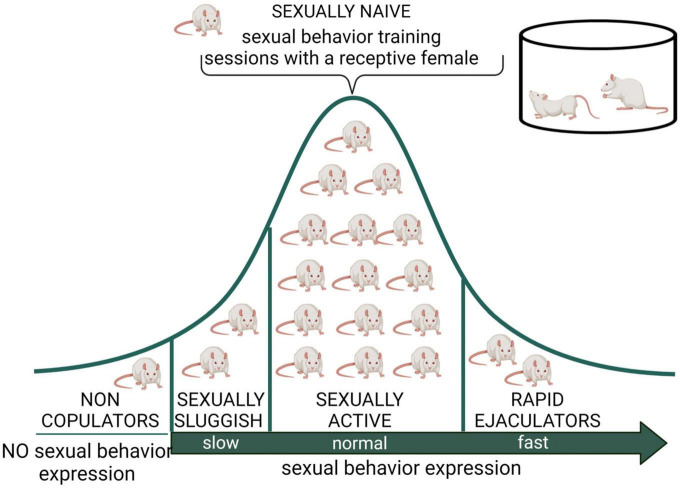
FIGURE 3.
Distribution of male rat sexual populations. When sexually naïve male rats are exposed to a receptive female, most animals will display sexual behavior and its copulatory pattern will become stable after several training sessions. However, there is an intra-specific variability in this species, expressed in at least three subpopulations in terms of sexual behavior expression. The non-copulating male rat, representing around 20% of the population, is constituted by apparently normal and healthy animals that will not mate despite repeated exposure to sexually receptive females (Beach, 1942). The sexually sluggish male, whose incidence is highly variable but always present in rat populations, requires long latencies to initiate copulation and to achieve ejaculation (e.g., with ejaculation latencies longer than 30 min) that are not reduced by repeated sexual experience. The rapid ejaculators are animals that ejaculate in extremely short periods of time and therefore achieve 4–5 ejaculations in 30 min (normal males usually display a couple of ejaculations in that period) (Pattij et al., 2005). Non-copulating, sexually sluggish and rapid ejaculating male rats are naturally occurring sub populations that might model human sexual dysfunctions such as male hypoactive sexual desire disorder and asexuality, lifelong delayed ejaculation, and premature ejaculation, respectively. Created with BioRender.com.