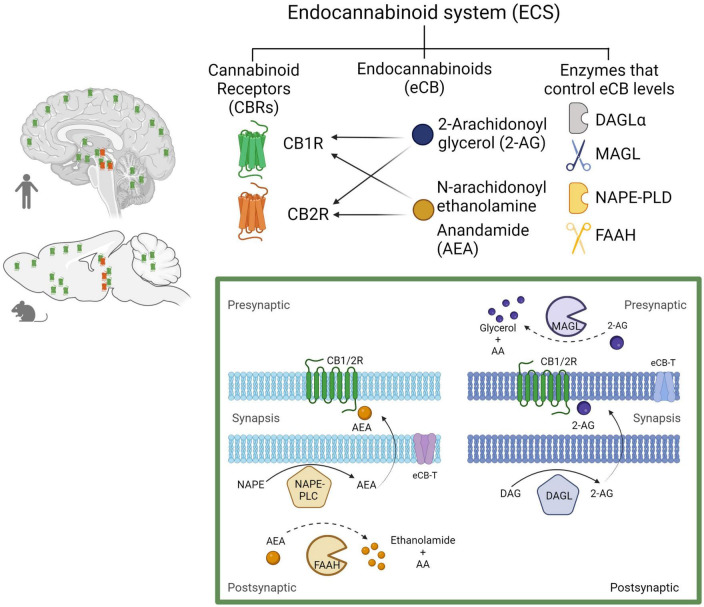
FIGURE 4.
The endocannabinoid system. Composed by two Gi/o-coupled cannabinoid receptors (CB1R and CB2R), their endogenous ligands (2-AG and AEA), and the enzymes involved in their synthesis (DAGLα and NAPE-PLD) and degradation (MAGL and FAAH). In the human and rodent brains, the CB1R is highly expressed in neurons, while the CB2R is mainly expressed in microglial cells in discrete brain areas as represented (CB1R in green and CB2R in red). Biosynthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids: eCBs are synthetized from membrane phospholipid precursors. N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide, AEA) is generated from its membrane precursor N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE) by a phospholipase D (NAPE–PLD). AEA is metabolized into ethanolamide and arachidonic acid (AA) by the action of the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) (Di Marzo et al., 1994). 2-AG is synthetized from membrane inositol phospholipids by a phospholipase C (PLC) producing diacylglycerol (DAG), which is hydrolyzed by the diacylglycerol lipase α (DAGLα). 2-AG degradation by monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) into glycerol and AA accounts for ≈ 85% of its breakdown (Sugiura et al., 1995). Created with BioRender.com.