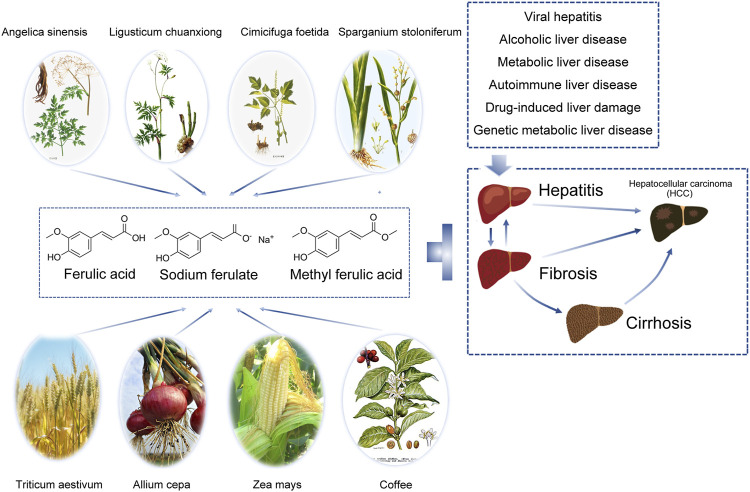
FIGURE 1.
Ferulic acid and its derivatives are widely distributed and can protect the liver by inhibiting liver injury in various ways. In the hepatitis-liver fibrosis/liver cirrhosis-liver cancer trilogy, various damage factors including viral infection, toxicants and drugs, alcoholic hepatitis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, cholestatic cirrhosis, autoimmune liver disease, genetic metabolic diseases, etc., cause hepatocyte necrosis or apoptosis, release a variety of cytokines, activate hepatic stellate cells and Kupffer cells, and lead to chronic inflammation. Liver fibrosis is the early stage of inflammatory stimulation and injury repair, which is reversible to some extent. When the pathogenic factors were removed, apoptosis occurred in activated hepatic stellate cells, collagen synthesis decreased and degradation increased, and liver structure and function recovered. If the injury and chronic inflammation persist, it can eventually develop into liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Ferulic acid can play a protective effect on many types of liver diseases in many ways.