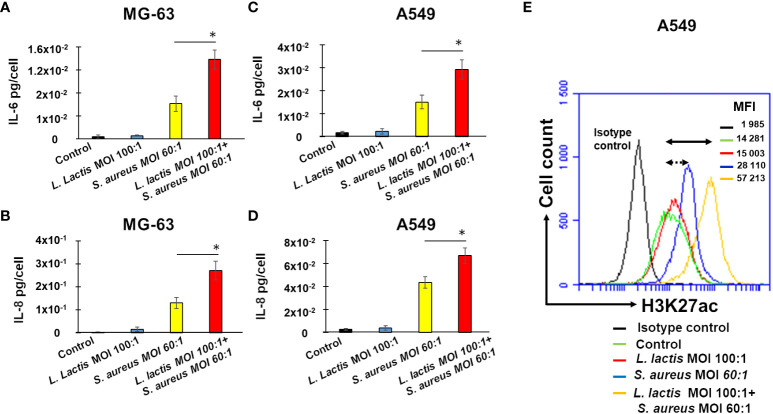
Figure 8.
Pre-exposure of MG-63 cells or A549 cells to L. lactis increases IL-6 and IL-8 production upon a stimulation with S. aureus with a positive correlation to H3K27 acetylation. Osteoblast-like MG-63 cells or lung epithelial A549 cells (20,000 cells/well) were seeded in wells of 24-well plates. Afterwards, cells were exposed either to L. lactis or to the cultivation medium for 24 h, followed by the incubation for 5 days before being exposed to S. aureus (MOI 60:1), as described in Material and Methods. The production of IL-6 and IL-8 was quantified in corresponding supernatants by ELISA and normalized by the number of cells in each well (A–D). Cell supernatants were collected (i) from control untreated cells at the end of the experiment (black bar graphs), (ii) from cells exposed to L. lactis (MOI 100:1), followed by a 5-day resting time and an additional 24 h (bleu bar graphs), (iii) from cells exposed to the cultivation medium for 24 h, followed by a 5-day resting time before an exposure to S. aureus (MOI 60:1) (yellow bar graphs), and (iv) from cells exposed to L. lactis (MOI 100:1), followed by a 5-day resting time before an exposure to S. aureus (MOI 60:1) (red bar graphs. Data are presented as mean +/- SD. The differences among the groups corresponding to different treatments were assessed by analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by a Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference test in R software. (*) P-values ≤ 0.05 were considered to be significant. For the evaluation of the level of H3K27 acetylation the remaining A549 cells after supernatants collection were used for flow cytometry analysis (E) as described in Material and Methods. Briefly, cells were treated with Trypsin/EDTA, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde/PBS followed by permeabilization in 0.1% Triton/0.5% BSA/PBS. Cells were subsequently incubated with anti-H3K27ac antibody diluted in PBS/2%BSA (1:50) for 1 h. An isotype control antibody was used to exclude nonspecific binding. Cells were then resuspended in PBS and were analyzed for H3K27 acetylation using an Accuri C6 flow cytometer (FL2 channel). Data were collected from 20,000 cells and analyzed using the CFlow software. Cells were analyzed using FSC-A x SSC-A plot. The major density of events was captured by the gate. The events corresponding to debris, cell fragments, and pyknotic cells were eliminated. Values shown on the right side of the graph refer to the respective mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs). A black graph corresponds to the isotype control, a green graph corresponds to control untreated cells, a red graph corresponds to cells exposed to L. lactis, followed by a 5-day resting time and an incubation for additional 24 h, a bleu graph corresponds to cells exposed to the cultivation medium for 24 h, followed by a 5-day resting time before being exposed to S. aureus, an yellow graph corresponds to cells exposed to L. lactis followed by a 5-day resting time before being exposed to S. aureus at MOI 60:1. Double arrow shows the shift between the fluorescence corresponding to the level of acetylation in control untreated cells (green line) and L. lactis-pretreated cells (MOI 100:1) followed by the exposure to S. aureus at MOI 60:1 (yellow line). Dotted double arrow shows the shift between the fluorescence corresponding to the level of acetylation in control untreated cells (green line) and S. aureus-treated cells (blue line). Two independent experiments in triplicate were performed. The results of the one representative experiments is shown.