FIGURE 1.
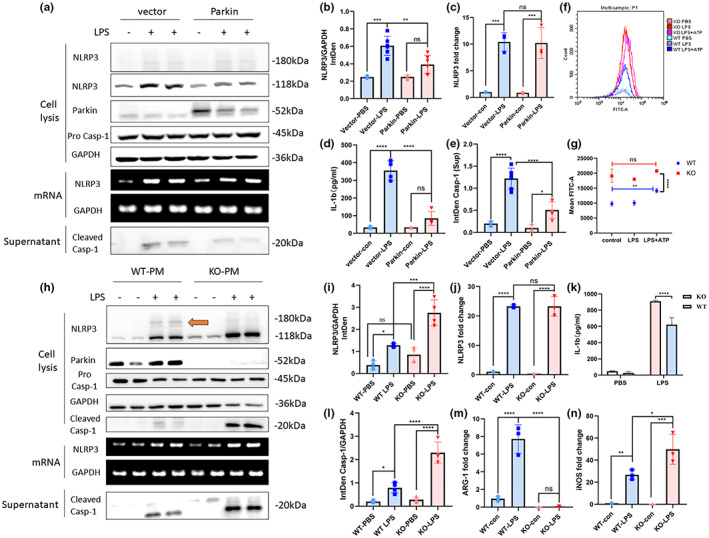
Parkin regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation. (a) Overexpression of Parkin in BV2 cells alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and the downstream inflammatory response but does not change the NLRP3 mRNA level. (b, i) Statistical analysis of the NLRP3 integrated density of WB experiments in BV2 cells (b) and PM (i). (d, k) ELISA of IL‐1β in the supernatant of BV2 cells (d) and PM (k). (c, j) qPCR of NLRP3 in BV2 (c) and PM (j). (e) Statistical analysis of cleaved Caspase‐1levels in supernatant of BV2. (f) Mitochondrial ROS levels of WT and Parkin KO PM quantified by flow cytometric analysis. (g) Statistical analysis of mean FTIC‐A in flow cytometric experiments. (h) Parkin KO exacerbates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and the downstream inflammatory response but does not alter the NLRP3 mRNA level. (l) Statistical analysis of the cleaved Caspase‐1 integrated density of WB experiments in PM. (m, n) qPCR of ARG‐1, and iNOS in PM. The orange arrow points out the post‐translational band of NLRP3. NLRP3, NOD‐, LRR‐, and pyrin domain‐containing 3; WB, Western blot; PM, primary microglia; ELISA, enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay; IL‐1β, interleukin 1 beta; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; ROS, reactive oxygen species; WT, wild‐type; KO, knockout; ARG‐1, arginase 1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; ns, not significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
