Figure 1.
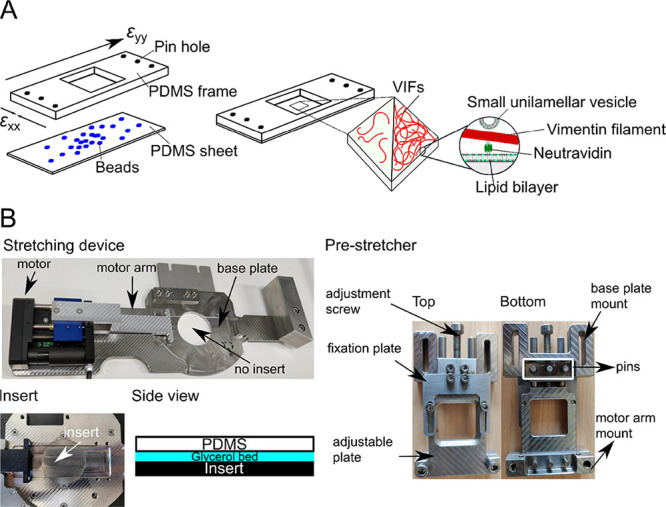
Stretching device. (A) (Left) PDMS chamber consisting of a PDMS frame with pin holes to attach the uniaxial stretching device and a PDMS sheet (thickness: ∼200 μm) with embedded fluorescent beads. Biotinylated VIFs at two different densities are bound to the PDMS-supported lipid bilayer harboring biotinylated lipids via biotin–neutravidin–biotin linkages. (Right) SUVs without biotinylated lipids serve as lipid reservoirs during stretching. (B) Components of the uniaxial stretching device. The pre-stretcher holding the PDMS chamber is mounted on the stretching device. For AFM measurements, an insert is placed in the center of the stretching device to close the hole, and a glycerol bed is placed between the PDMS chamber and the insert to dampen external vibrations.
