Fig. 1.
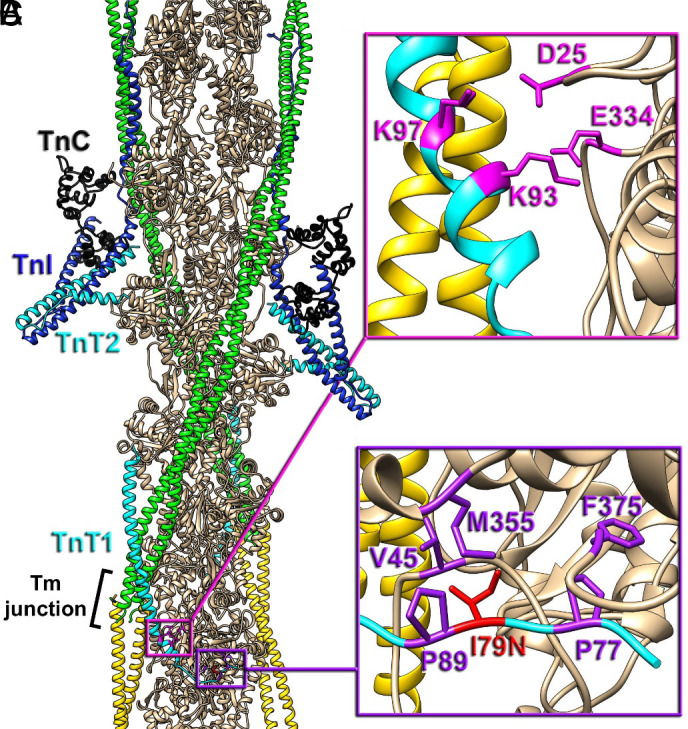
Positioning of cTnT-I79N within the cardiac TF. (A) The molecular organization of the cardiac TF in relaxed state (3, 10). Actin subunits (tan) are shown with a pair of Tm cables (green and yellow) and a pair of Tn complexes comprised of TnC N- and C-lobes (black), TnI (blue), and TnT (cyan) with its N-terminal region (TnT1) extended to the Tm junction region (black bracket). The TnT1 ionic (magenta box detailed in panel B) and hydrophobic interactions (purple box detailed in panel C with actin) anchor the Tm junction region to the actin filament to presumably stabilize the relaxed state of the thin filament (10). (B) Ionic interactions of TnT1 K93 and K97 with E334 and D25 of actin (magenta atoms) link TnT1 helix to the actin surface. (C) Positioning of TnT1 is further stabilized by the hydrophobic interactions between V45, M355, F375 actin residues and P77, I79, P89 TnT1 residues (purple atoms). cTnT-I79 (red atoms), when replaced to N79 presumably disrupts the hydrophobic cluster and weakens the interaction of TnT1 with actin.
