Fig. 5.
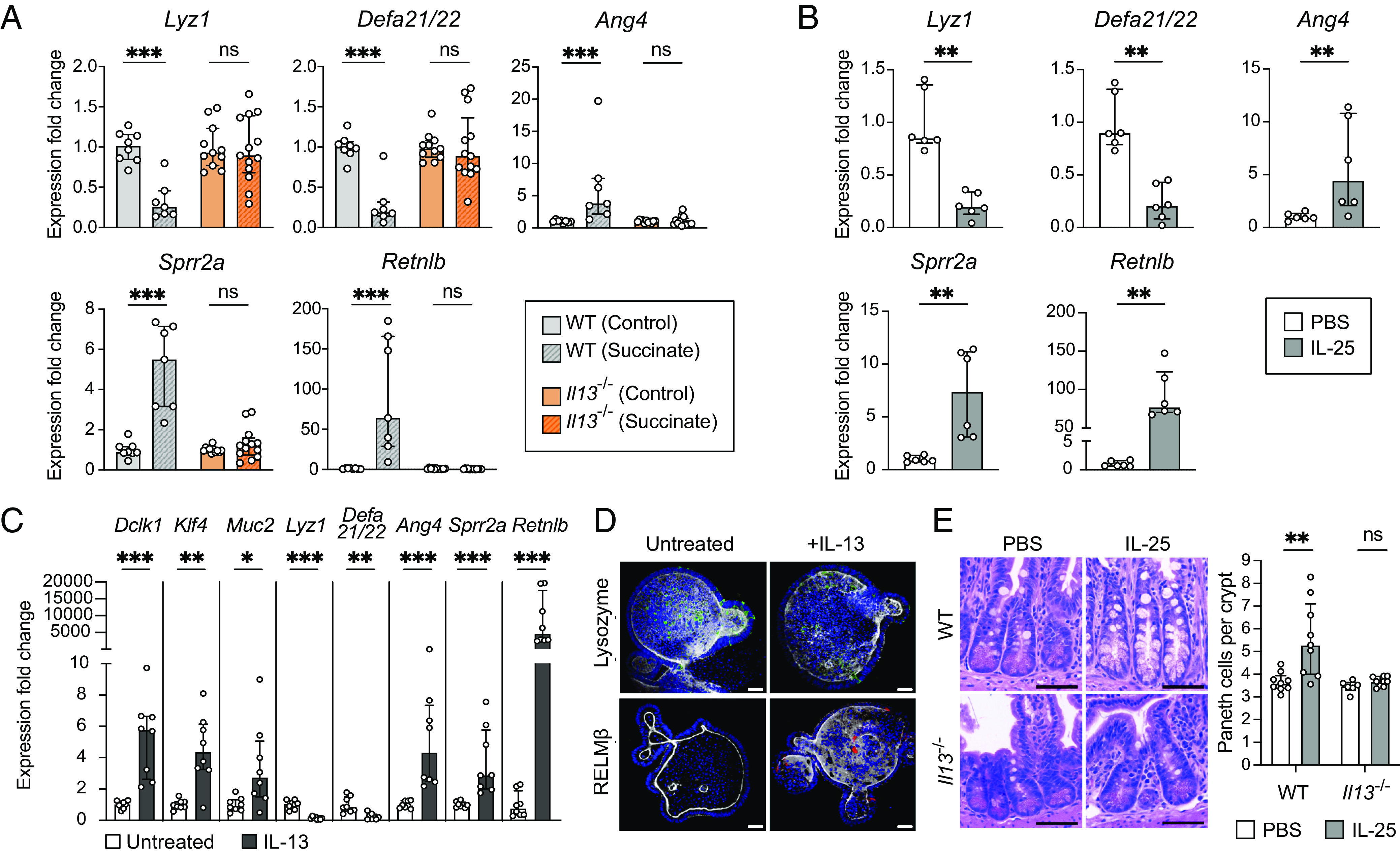
The type 2 cytokine IL-13 is critical for small intestinal Paneth cell hyperplasia and changes to AMP expression downstream of tuft cell stimulation. (A) Expression of representative AMP genes determined by qRT-PCR in the ileal epithelial fraction of control or succinate-treated WT and Il13−/− mice (n = 7 to 13 mice per group). (B) Expression of representative AMP genes determined by qRT-PCR in the ileal epithelial fraction of WT mice IP-injected with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or IL-25 (n = 6 mice per group). (C) Expression of Dclk1 (tuft cell marker), Klf4 and Muc2 (goblet cell markers), and representative AMP genes determined by qRT-PCR in untreated or IL-13-treated ileal organoids (n = 8 samples per group). (D) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of untreated or IL-13-treated ileal organoids. Nuclei (blue), F-actin (white), LYZ (green), RELMβ (red). (Scale bar: 30 µm.) (E) Left: Representative images of H&E-stained sections of the ileal crypts from PBS- or IL-25-injected WT or Il13−/− mice. (Scale bar: 50 µm.) Right: Average number of Paneth cells per crypt in the ilea of PBS- or IL-25-injected WT or Il13−/− mice (n = 6 to 9 mice per group). For qRT-PCR data, relative expression normalized to Gapdh. For all panels, center values = median; error bars = IQR. Significance was determined using the Mann–Whitney U test. ns = no significance, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
