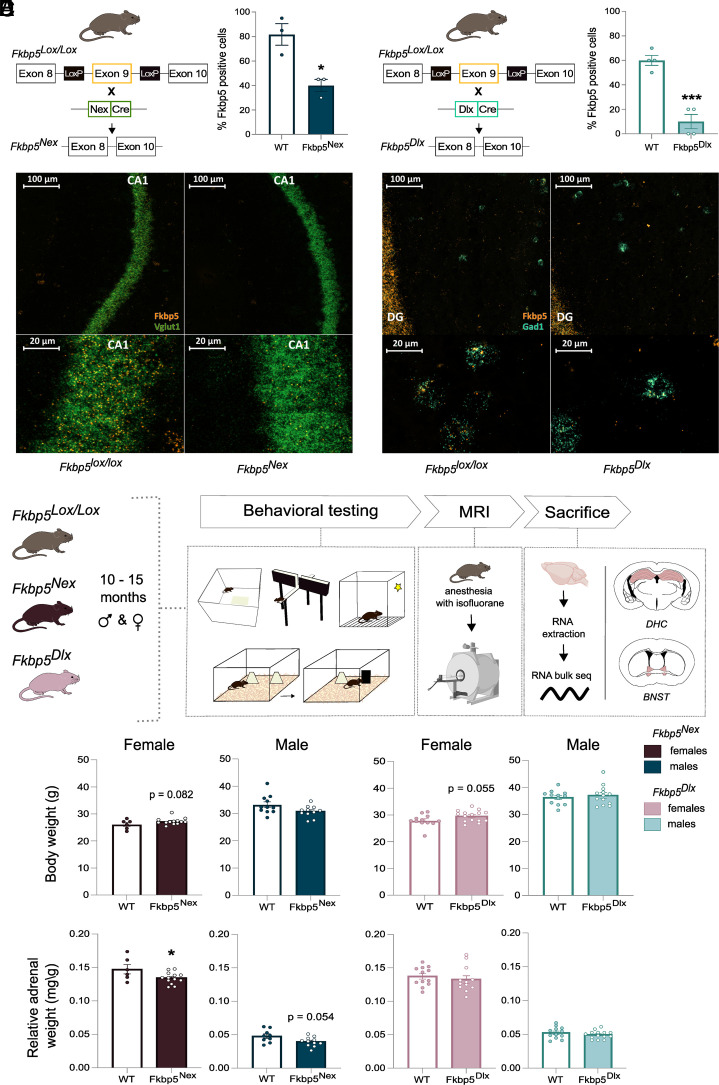
Fig. 1.
Experimental setup and physiological measurements. By breeding Fkbp5lox/lox mice, in which exon 9 of the Fkbp5 gene is flanked by two loxP sites, with (A) Nex-Cre mice, a significant reduction of Fkbp5 mRNA in glutamatergic forebrain neurons was achieved. (B) Breeding of Fkbp5lox/lox mice with Dlx5/6-Cre mice resulted in a significant loss of Fkbp5 mRNA in GABAergic forebrain neurons. RNA scope confocal images of the DHC illustrated these significant reductions of Fkbp5 (orange panel) in glutamatergic CA1 neurons (Vglut1; green panel) and GABAergic interneurons (Gad1; blue panel). Ten- to fifteen-month–old Fkbp5Nex and Fkbp5Dlx mice of both sexes were exposed to a behavioral paradigm including tasks for anxiety, neutral and stressed cognition, followed by an MRI scanning procedure (C). After completion of the experiments, mice were sacrificed and tissue from the DHC and the BNST was collected for RNA bulk sequencing purposes. Analyses of physiological parameters revealed sex specific effects for body weight (D) and cell dependent changes in relative adrenal weight (E). Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *P <0.05, ***P < 0.001.