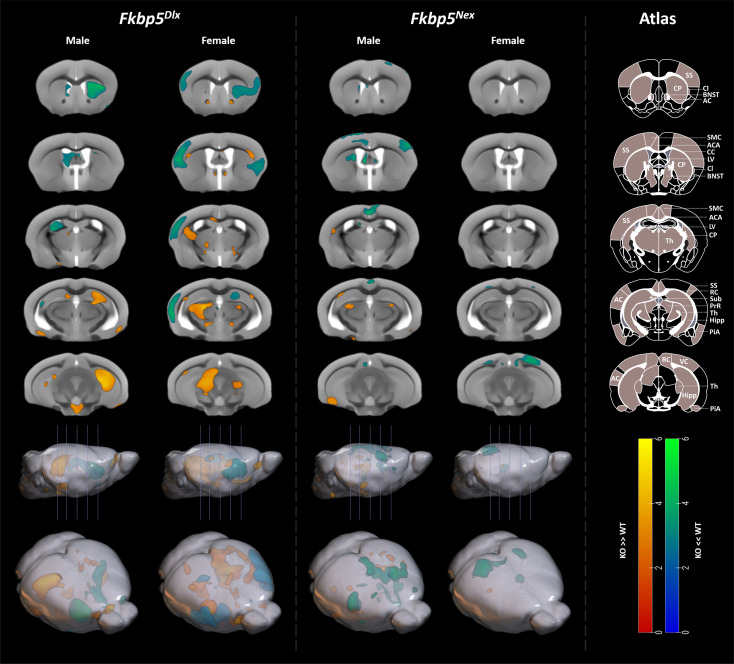
Fig. 3.
Loss of Fkbp5 leads to the largest structural changes when restricted to GABAergic neurons of the forebrain. Data from the T2*-weighted MRI scan revealed underlying structural consequences of loss of Fkbp5 in either glutamatergic or GABAergic neurons of the forebrain, with the largest and most significant changes in Fkbp5Dlx male and female mice. For Fkbp5Dlx male mice, large and strongly significant increases in GM volume were found in the bilateral hippocampus compared to Fkbp5lox/lox controls, whereas GM volumes were significantly decreased in the caudoputamen and lateral ventricle. Female Fkbp5Dlx mice had larger GM volumes in the thalamus than their Fkbp5lox/lox controls and strongly significant smaller GM volumes in the somatosensory cortex, claustrum, and auditory cortex. In addition, a number of WM structures were altered such as the corpus callosum and some GM areas around the BNST, although these clusters did not survive FWE correction. Furthermore, Fkbp5Nex male mice had significantly smaller GM volumes in bilateral regions of the motor cortex extending to the anterior cingulate area vs. Fkbp5lox/lox controls and uncorrected increased GM volumes were found in the left caudoputamen, right piriform area, bilateral dorsal thalamus and left ventral subiculum. Female Fkbp5Nex mice had decreased GM volumes in the right anteriormedial visual area. Scales represent Z-scores. Yellow-red scale: KO > WT, Greenblue scale: KO < WT. AC = Auditory Cortex, ACA = Anterior Cingulate Area, CC = Corpus Callosum, Cl = Claustrum, CP = Caudoputamen, Hipp = Hippocampus, LV = Lateral Ventricle, PiA = Piriform Area, PrR = Pretectal region, RC = Retrosplenial Cortex, SMC = Sensorimotor cortex, SS = Somatosensory Cortex, Sub = Subiculum, Th = Thalamus, VC = Visual Cortex.