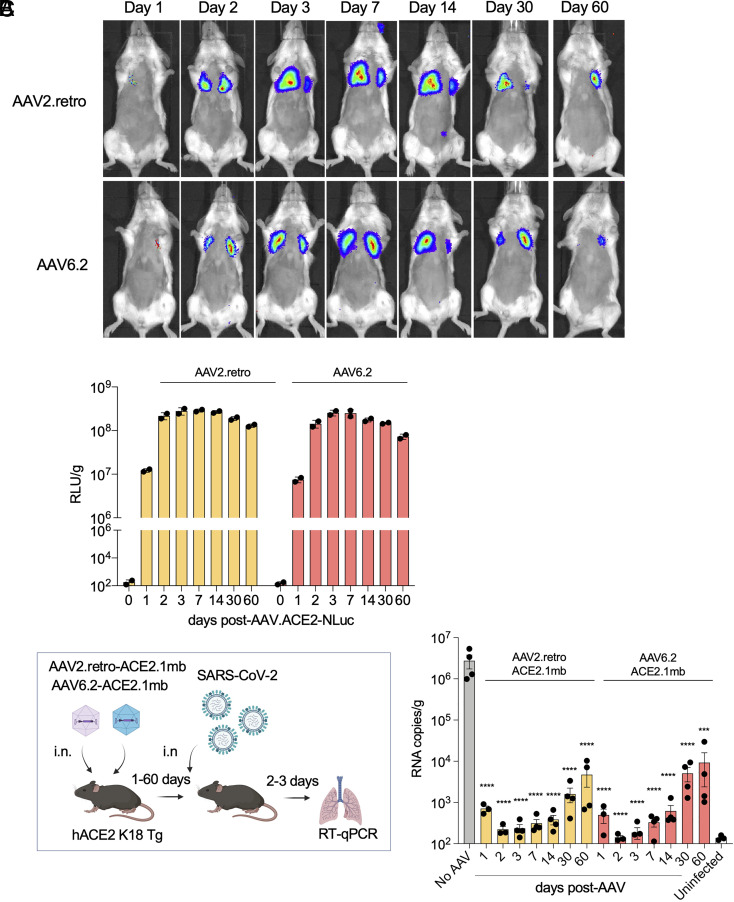
Fig. 3.
Durable vectored immunoprophylaxis by decoy-expressing AAV vectors. (A) Balb/c mice (n = 3) were injected i.n. with decoy-luciferase fusion protein-expressing AAV vectors (1 × 1012 vg). Luciferase activity was visualized by live imaging over 60 d at the indicated time points. Representative images of a mouse from each group are shown. (B) Luciferase activity in lung tissue homogenates from mice treated with the decoy-luciferase-expressing AAV vectors (n = 2) was measured over the time course. (C) The experimental scheme to test the durability of AAV vectored immunoprophylaxis is diagrammed (Left). hACE2 K18 Tg (n = 4) were injected with AAV decoy. At 1-, 2-, 3-dpi, the mice were challenged with SARS-CoV-2 (2 × 104 PFU) and viral RNA in the lungs was quantified. The results are shown as a histogram (Right). SARS-CoV-2-infected/AAV-untreated (No AAV) and AAV-untreated/SARS-CoV-2-uninfected (Uninfected) controls are shown. CIs are shown as mean ± SD. ****P ≤ 0.0001.