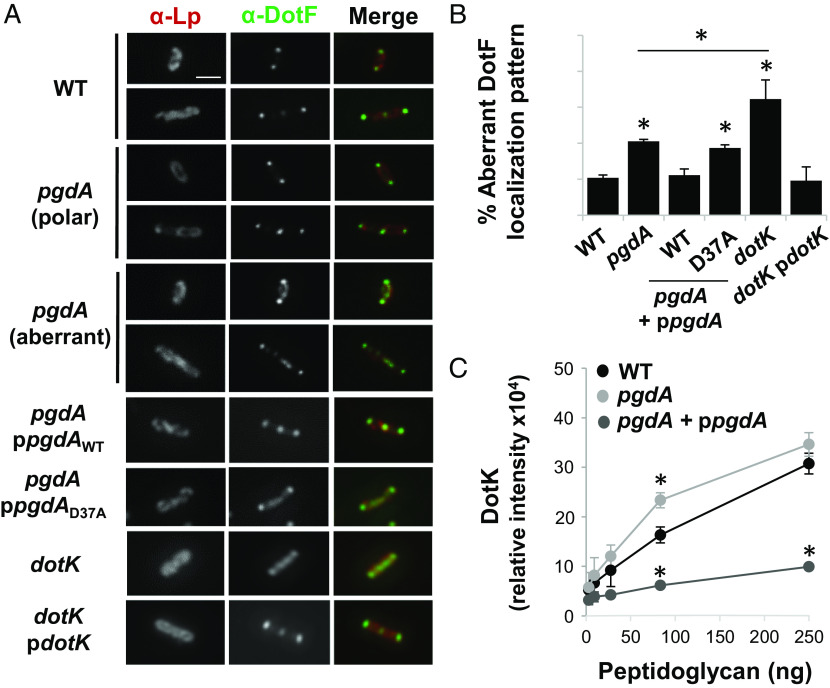
Fig. 5.
PgdA promotes polar localization of the Dot/Icm secretion system by modulating DotK binding to peptidoglycan. (A) ΔpgdA and ΔdotK mutant bacteria show mislocalization of Dot/Icm. Bacteria were grown to late exponential phase, fixed, stained for DotF, and visualized by fluorescence microscopy. (Scale bar indicates 2 μm.) (B) The number of bacteria in A exhibiting aberrant (non-polar) distribution of the DotF was scored. Data are the mean ± SD of 3 biological replicates, scoring an average of 300 to 500 bacteria per replicate. *P < 0.001. (C) PgdA restricts DotK binding to peptidoglycan. Purified DotK was incubated with varying amounts of peptidoglycan isolated from the indicated strains, peptidoglycan was collected, and the amount of bound DotK based on western analysis (SI Appendix, Fig. S19B) was quantified. Data are the mean ± SD of 3 biological replicates, each consisting of independently isolated peptidoglycan. *P < 0.05. An asterisk indicates a two-tailed Student’s t test P value as indicated relative to the wild-type (WT) strain.