Figure 5.
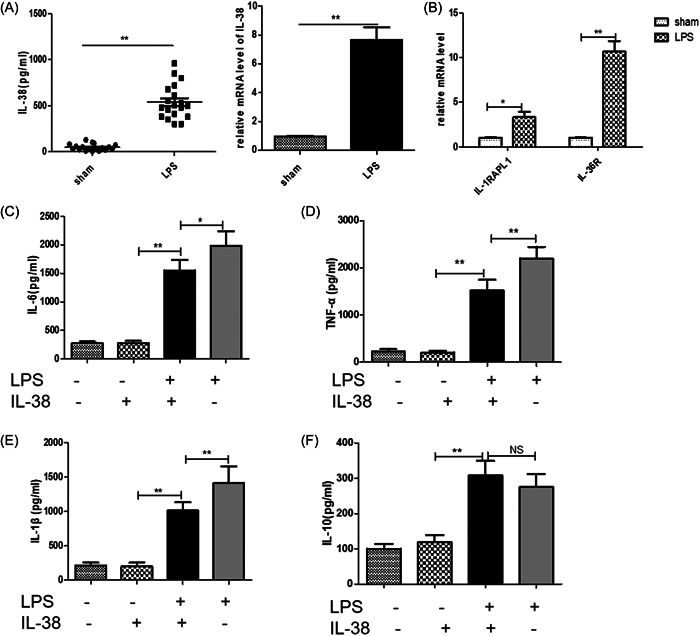
Interleukin‐38 (IL‐38) inhibited lipopolysaccharide (LPS)‐induced macrophage inflammation. Macrophages were incubated with 1 μg/mL LPS and/or 100 ng/mL IL‐38 for 24 h. (A) IL‐38 expression level was assessed by enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (in cultured supernatants) and real‐time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in cultured macrophages. (B) Real‐time PCR determined messenger RNA (mRNA) expression level of IL‐38 receptors. The expression levels of IL‐6 (C), tumor necrosis factor‐α (TNF‐α) (D), IL‐1β (E), and IL‐10 (F) were measured by ELISA in cultured supernatants of different treatment groups (each group n = 6–8). *p < .05; **p < .01; NS, not significant.
