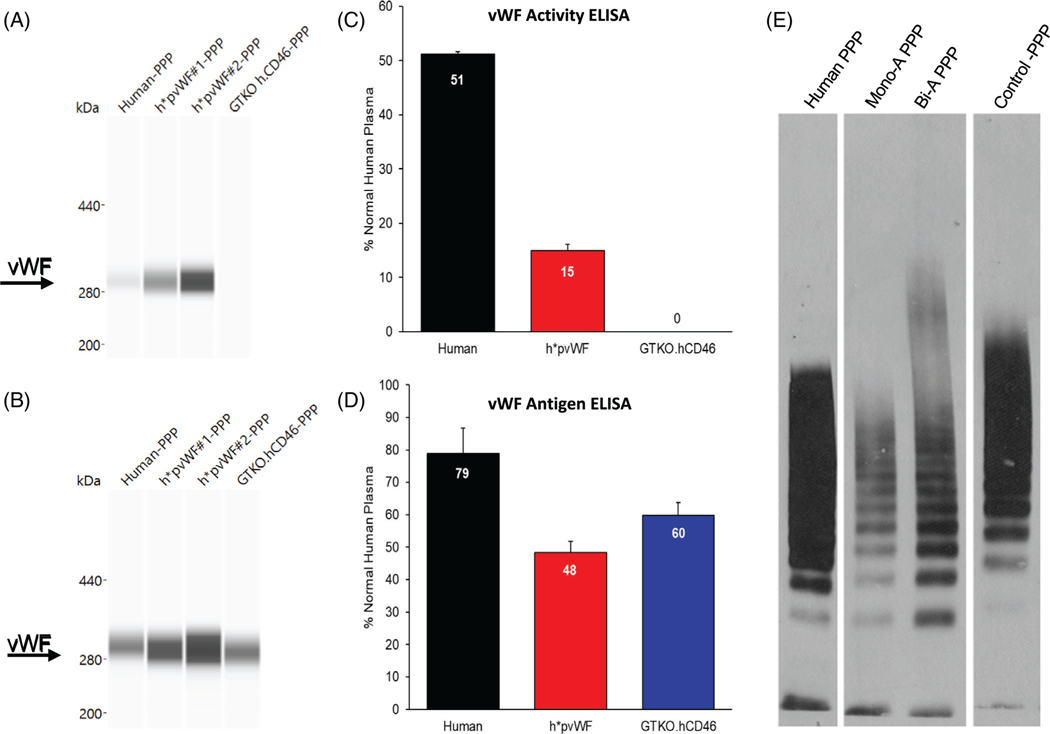
FIGURE 2.
vWF protein expression by Western blot and ELISA in plasma. Capillary Western blots were run on the WES system using platelet-poor plasma (PPP). (A) Monoclonal antibody specific to hvWF glycoprotein Ib (GPIb)-binding domain detected hvWF and h*pvWF but not pvWF from GTKO.hCD46 pigs. (B) Polyclonal antibody to full-length hvWF detected hvWF, h*pvWF, and GTKO.hCD46 porcine vWF (pvWF). vWF activity and antigen were assayed on PPP using two hvWF ELISA kits. Each assay included plasma from three h*pvWF pigs. Human (n = 1) and GTKO.hCD46 pig (n = 1) samples were included as controls. Samples were run twice in duplicate. Mean and SD assay results are shown. (C) The vWF activity ELISA measures vWF using a monoclonal antibody specific to the hvWF GPIb-binding domain. Measurable vWF activity was found in plasma from human and h*pvWF pigs but not from control GTKO.hCD46 pigs. vWF activity in both human and h*pvWF PPP was in the normal human range for the assay (1.7%–57.98%; mean 26.5%). (D) The vWF antigen ELISA measures hvWF using an antibody that cross-reacts with pvWF. Measurable vWF antigen was found in plasma from human, h*pvWF pigs, and GTKO.hCD46 pigs. vWF antigen levels in human, h*pvWF, and GTKO.hCD46 pigs was within the normal human range for the assay (47%–197%; mean 106%). (E) vWF multimer patterns in PPP. Membranes were probed with hvWF antibody. vWF from human, h*pvWF, and control GTKO.hCD46 pigs were capable of forming multimers in this assay