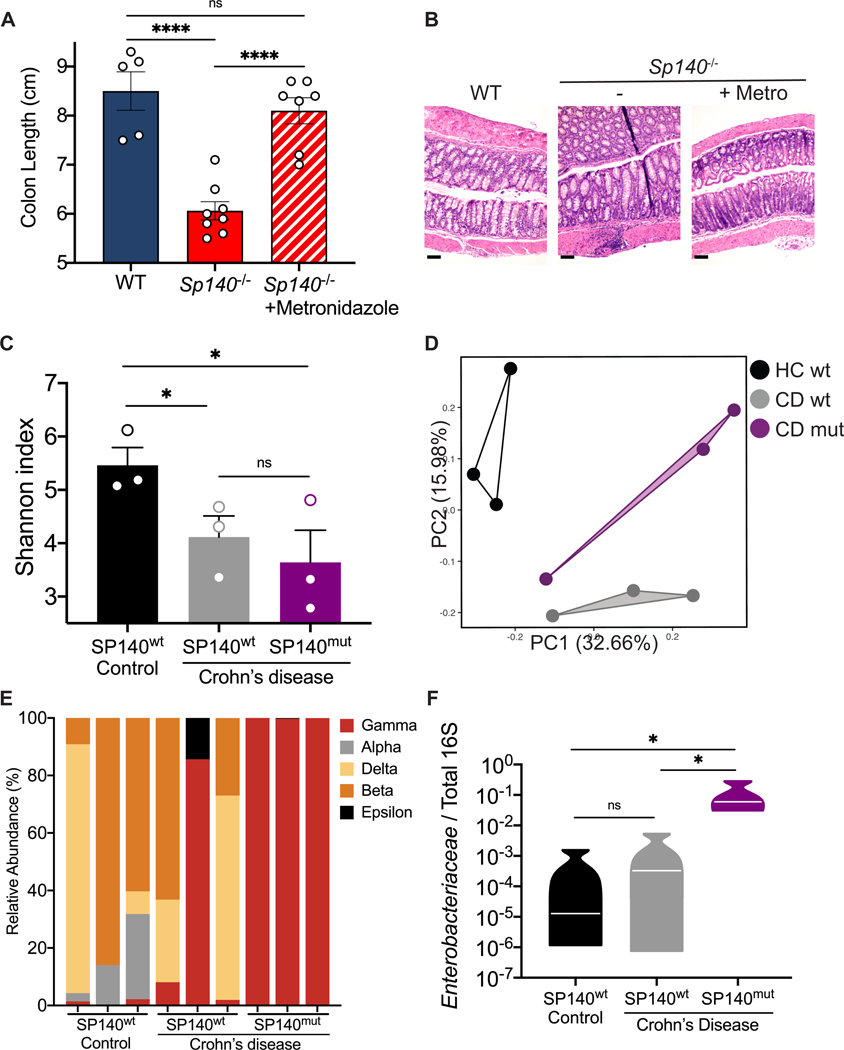
Figure 4. CD-associated SP140 loss-of-function variant associates with increased intestinal Enterobacteriaceae in humans.
(A) Day 12 colon lengths of WT, Sp140−/−, and Sp140−/− mice treated with or without metronidazole and administered 2% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS). (B) Representative hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of day 12 distal colon tissue after 2% DSS administration to WT, Sp140−/−, and Sp140−/− mice treated with metronidazole (metro). (C) Diversity of fecal bacterial communities of healthy controls, Crohn’s disease (CD) patients expressing wildtype SP140 (SP140wt), and CD patients bearing the common SP140 genetic variant (SP140mut). (D) Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCA), P<0.05, PERMANOVA on unweighted UniFrac distance. (E) Distribution of bacterial class operational taxonomic units presented as relative abundance of Proteobacteria in each sample. (F) Expression of Enterobacteriaceae 16S rRNA relative to total 16S rRNA in human stool. Error bars represent means ± SEM. n.s., not significant, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001; (A-B) n=5–8; (C-F) n=3, one-way ANOVA.