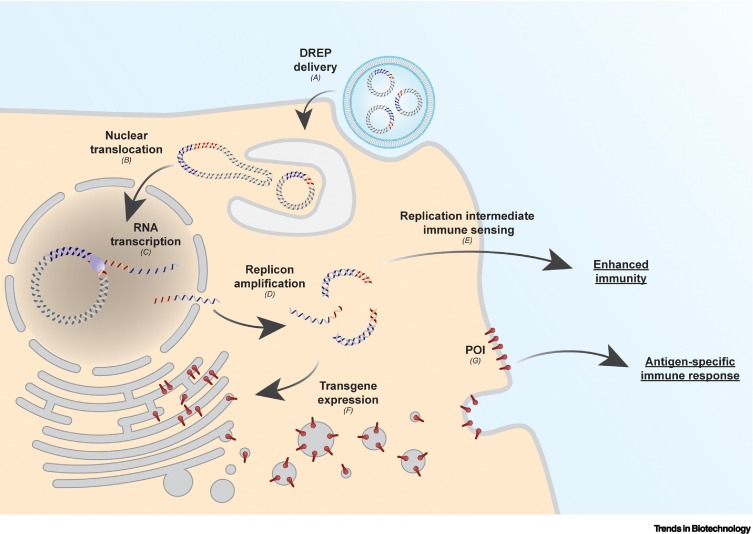
Figure 3.
Schematic overview of heterologous gene expression using a liposomal-delivered DNA-launched RNA replicon (DREP).
(A) Upon liposomal delivery to a cell, (B) the DREP migrates to the nucleus where (C) it serves as a template for the RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription of replicon RNA. (D) Subsequently, the replicon RNA is transported to the cytoplasm where the self-amplification, mediated by replicase proteins, occurs. (E) During amplification, cellular sensors recognize amplification intermediates (double-stranded RNA), enhancing host immunity. (F) At the same time, translation of the replicon RNA produces the protein of interest (POI). (G) This will induce an antigen-specific immune response.