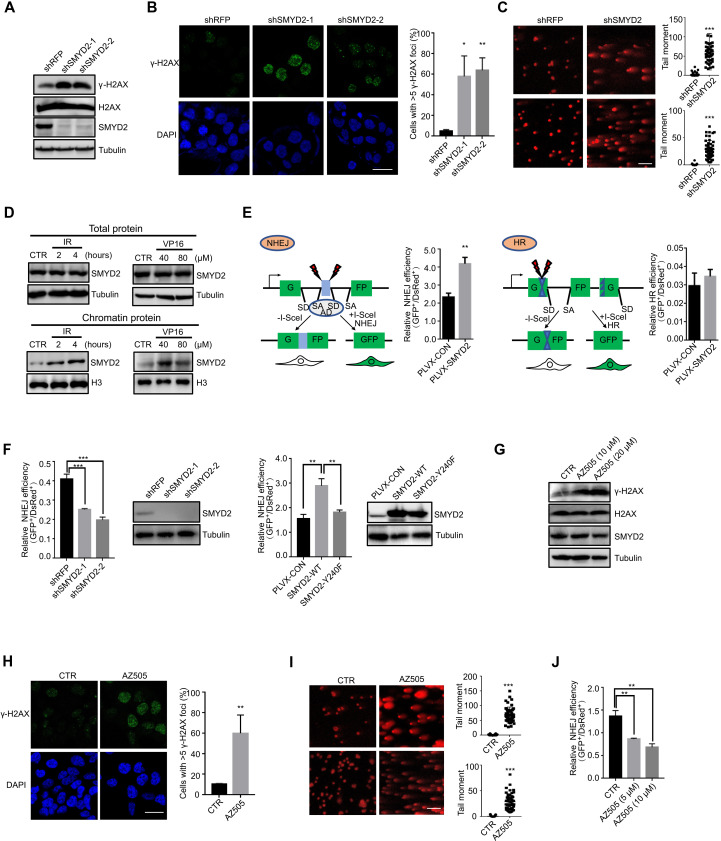
Fig. 1. SMYD2 is required for DDR.
(A) Immunoblot of the expression levels of γ-H2AX in SMYD2-depleted HCT116 cells. (B) Representative fluorescence images and quantification of γ-H2AX immunostaining in cells with and without SMYD2. Scale bars, 25 μm. Green, γ-H2AX; blue, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). (C) Representative fluorescence images and quantification of tail moments in HCT116 and CT26 cells with and without SMYD2 as determined by a comet assay. Scale bars, 100 μm. (D) Immunoblot of endogenous SMYD2 in total proteins treated with IR at 10 grays (Gy) and released for 2 or 4 hours and etoposide (VP16) at 40 or 80 μM for 4 hours of HCT116 cells (top). Immunoblot of endogenous SMYD2 in chromatin proteins treated with IR at 10 Gy and released for 2 or 4 hours and etoposide (VP16) at 40 or 80 μM for 4 hours of HCT116 cells (bottom). (E) Diagram of the NHEJ and HR reporter assay. Effects of SMYD2 overexpression on the efficiency of NHEJ and HR in I9a and H15c cells. (F) Effects of SMYD2 stably knockdown on the efficiency of NHEJ in I9a cells and immunoblot showing the knockdown efficiency of SMYD2 (left graph). Effects of SMYD2-WT/Y240F on NHEJ efficiency in I9a cells and immunoblot showing the expressed protein (right graph). (G) Immunoblot of the expression levels of γ-H2AX in AZ505-treated HCT116 cells. (H) Representative fluorescence images and quantification of γ-H2AX immunostaining in cells treated with and without SMYD2 inhibitor AZ505. Scale bars, 25 μm. Green, γ-H2AX; blue, DAPI. (I) Representative fluorescence images and quantification of tail moments in cells treated with and without SMYD2 inhibitor AZ505 at 20 μM as determined by a comet assay. Scale bars, 100 μm. (J) NHEJ efficiency of SMYD2 inhibition with its inhibitor AZ505 at indicated concentrations.