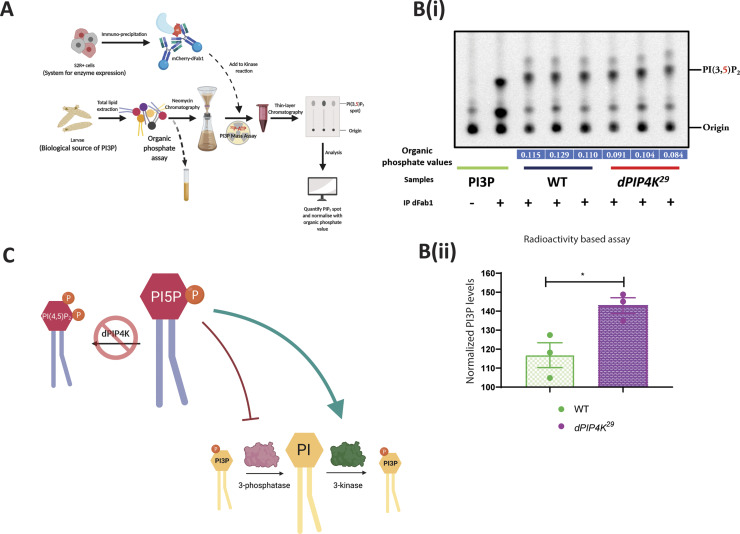
Figure S3. Drosophila PIP4K regulates in vivo PI3P levels.
(A) Schematic illustrating the methodology to assay PI3P by a dFab1-mediated radioactivity-based mass assay. dFab1 is purified from S2R+ cells by immunoprecipitation and used to convert PI3P from total lipid extracts obtained from larvae in the presence of ϒ32P-ATP to radiolabelled PI(3,5)P2 product which is finally analysed using TLC. A portion of the total lipid extract is used for organic phosphate assay to normalise for sample size. (B) (i) Autoradiograph of TLC ran with lipid samples from in vitro PI3P mass assay using WT and dPIP4K29 lipid samples. The first two lanes from the left are obtained from mass assay reactions using synthetic PI3P standard without or with addition of dFab1 enzyme, respectively. The origin spot and PI(3,5)P2 spots are marked. (B) (ii) Graph represents normalised PI3P levels. Briefly, the spot marked as PI(3,5)P2 on TLC in (B) is obtained by converting PI3P in the samples using immunoprecipitated dFab1 in the presence of ϒ32P-ATP are quantified using image analysis and then normalised to organic phosphate value (indicated in blue embedded text under TLC) to obtain normalised PI3P levels. Biological samples = 3, where each sample was made from five third instar wandering larvae. Unpaired t test with Welch correction showed P-value = 0.036. (C) Illustration depicting an indirect model where the increased PI3P levels in dPIP4K29 (denoted by a red cross on dPIP4K) can be explained by either an activation of PI 3-kinase activity (green arrow) or an inhibition of PI3P 3-phosphatase activity (red stubbed arrow).