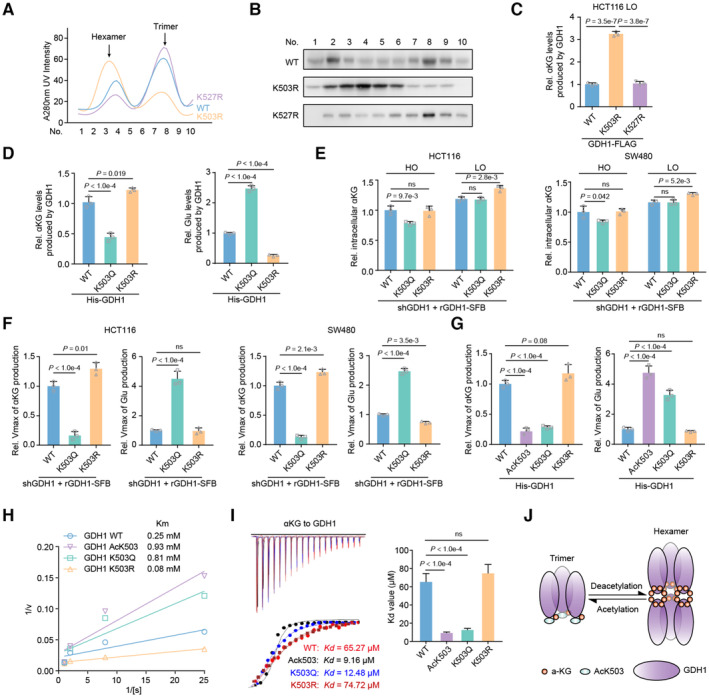
Figure 4. GDH1 acetylation at K503 reverses GDH1 dehydrogenase activity through decreased formation of GDH1 hexamers.
-
AGDH1‐FLAG (including WT and K503R and K527R mutants) was enriched and analyzed via fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC).
-
BImmunoblot analysis of GDH1‐FLAG levels at different time points.
-
CThe K503R mutation enhances GDH1 activity in producing αKG. FLAG‐tagged GDH1 was purified from HCT116 cells (n = 3).
-
DThe K503Q mutation reduces GDH1 activity leading to αKG production while enhancing the enzymatic activity leading to Glu production. His‐tagged GDH1 was purified from E. coli (n = 3).
-
E, FHCT116 or SW480 cells were depleted of endogenous GDH1 and rescued with SFB‐tagged rGDH1 WT, K503Q or K503R. The relative intracellular αKG concentration was measured under normoxia and hypoxia (E). rGDH1‐SFB proteins were enriched using M2‐FLAG beads to determine the Vmax of αKG production (F) (n = 3).
-
G–IHis‐GDH1 proteins (including WT, AcK503, K503Q and K503R) were purified from E. coli to determine the Vmax of αKG and Glu production (G). A Lineweaver–Burk plot was used to determine the Michaelis–Menten constant (Km) value for Glu production by the GDH1 proteins (H). V, reaction rate; [S], substrate concentration. ITC assays were performed with precipitated His‐GDH1 proteins and αKG (I) (n = 3).
-
JCartoon illustrating the working mechanism of the GDH1 acetylation‐mediated decrease in hexamers and the enhanced binding affinity to αKG.
Data information: Data are mean ± SD from the biological replicates (C–G, I). Statistics: one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test (C–G, I).
Source data are available online for this figure.
