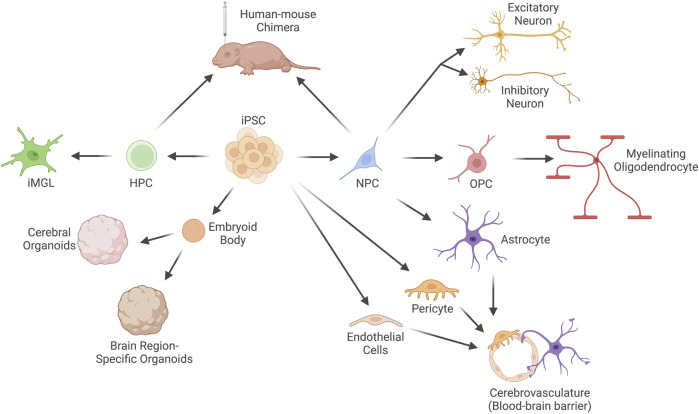
FIGURE 2.
Current techniques to differentiate human induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) into brain cell types. Human iPSCs can be differentiated into neural progenitor cells (NPCs), which are the progenitor cell for neurons (both excitatory and inhibitory), myelinating oligodendrocytes and their progenitors (oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, OPCs), and astrocytes. iPSCs can also be differentiated into the other two primary cell types of the blood-brain barrier (BBB): endothelial cells and pericytes, which can be co-cultured with astrocytes to recapitulate the BBB in vitro. Embryoid bodies can be formed from aggregates of iPSCs and cultured in unguided or guided conditions to generate cerebral organoids or brain region-specific organoids. Microglia-like cells (iMGLs) of the myeloid lineage can be differentiated from hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) in vitro. Alternatively, HPCs or NPCs can be engrafted into the brain of immunodeficient mice to generate human-mouse chimeras.