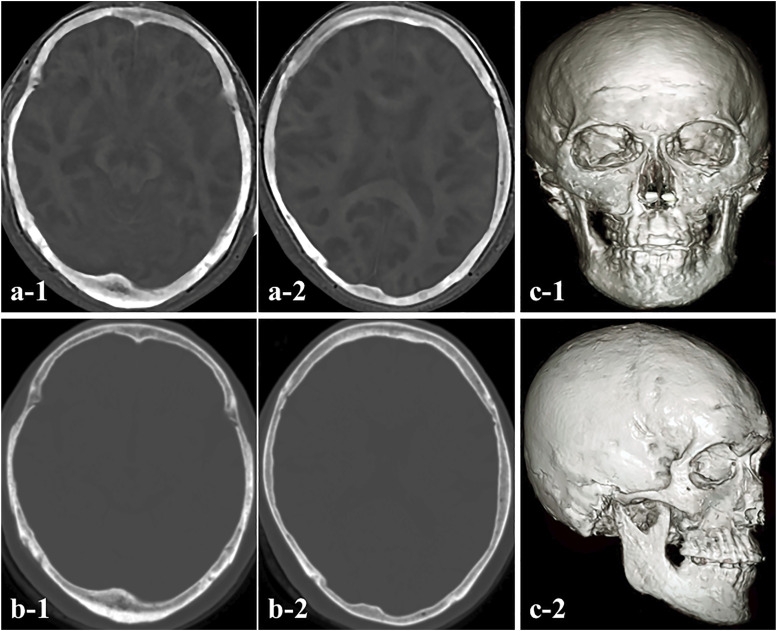
Figure 1.
(a) Bone images obtained with zero-echo-time (ZTE)-based magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). (b) Computed tomography (CT) showing axial views of a typical dataset for the skull region. The edges of the cranium acquired with the ZTE sequence were almost matched to the images obtained with CT, and no limbal distortion was observed. (c) 3D ZTE-based MRI model demonstrating cranial bone.