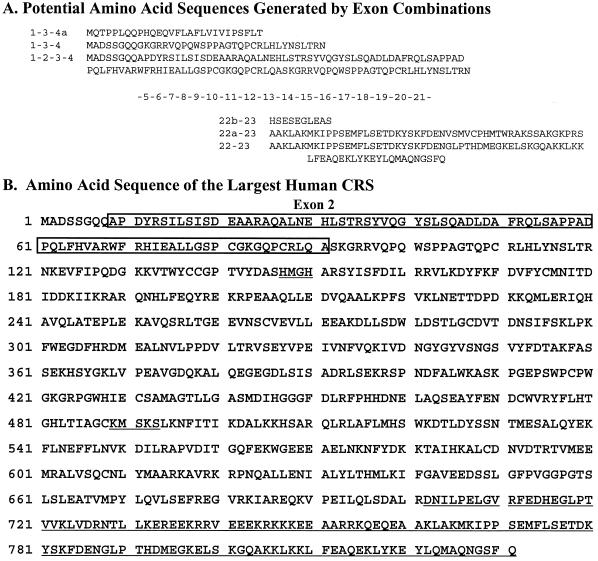
Figure 2.
Potential CRS isoforms and deduced amino acid sequence of the largest human CRS. (A) Amino acid sequences are shown based on potential combinations of exons. Analyses of genomic DNA, cDNA and EST sequences reveal 23 exons; one newly predicted exon (exon 2) and two alternatively spliced exons. Exon 4 has two splicing start points (4 and 4a) and exon 22 has two splicing start points and two end points (22, 22a, 22b and 22c). Thus, the N-terminus has four possible combinations of exon 2, exons 2–, 2+, 4 and 4a, and the C-terminus has four possible forms of exon 22. Translation start positions are different for combinations of 1-3-4 and 1-3-4a. Exon combinations 1-2-3-4a and 22c-23 are not shown because they would give the same results as sequences 1-3-4a and 22b-23, respectively. (B) The deduced amino acid sequence of the largest human CRS. A transcript containing exons 2, 4 and 22 would yield an 831 amino acid polypeptide. The residues from exon 2 are boxed and the C-terminal sequence different from the corresponding region of CRS in GenBank is underlined. The two class I signature sequences (HMGH and KMSKS) in the core domain are also underlined.