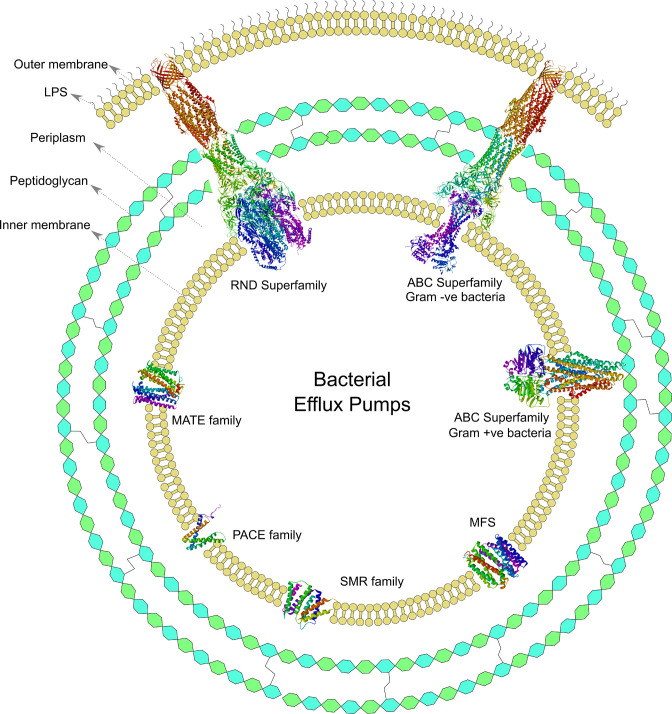
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of bacterial efflux pumps. All bacterial efflux pumps are located on the inner membrane. Gram-negative bacteria have three components in their cell envelope, i.e. outer membrane, peptidoglycan layer, and inner membrane. Gram-positive bacteria have only two components in their cell envelope, i.e. peptidoglycan layer and inner membrane. Representative structures from each family (superfamily) have been presented here. Currently, six types of efflux pump families have been identified in bacteria, i.e. ATP-binding cassette (ABC) superfamily, major facilitator superfamily (MFS), small multidrug resistance (SMR) family, proteobacterial antimicrobial compound efflux (PACE) family, multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) family, and resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) superfamily. The following PDB (Protein Data Bank) identifiers were used for depicting 3D structures; 2HYD for the ABC superfamily (Gram-positive); 3VVN for the MATE family; 4ZOW for MFS; 5NIK for the ABC superfamily (Gram-negative); 5V5S for RND superfamily; and 6WK9 for SMR family. Three dimensional structure of the PACE family (GeneBank ID: A1S_2063) was predicted using the ColabFold algorithm [119]. Then 3D structures were rendered using BIOVIA Discovery Studio Visualizer (Dassault Systems, France).