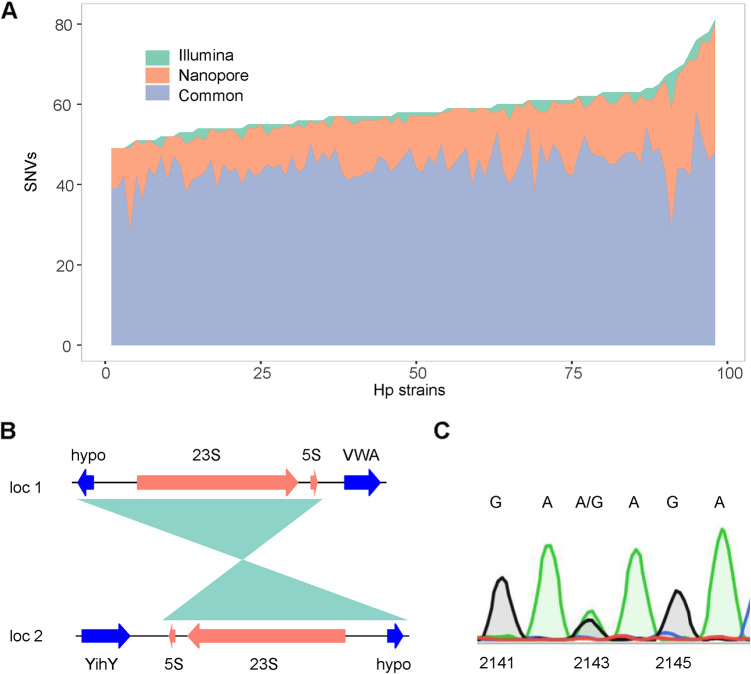
FIG 2.
Consistency of Illumina- and Nanopore-based sequencing in discovering SNVs of the H. pylori 23S rRNA gene and its heterozygous status. (A) Stacked area graph showing the SNVs identified using Illumina and Nanopore technologies. SNVs of 98 strains were determined using the Illumina-VarScan pipeline or the Nanopore-Clair3 pipeline. The SNVs determined using the two pipelines were then compared. Common, SNVs detected using both pipelines; Nanopore, SNVs detected using only the Nanopore-Clair3 pipeline; Illumina, SNVs detected using only the Illumina-VarScan pipeline. (B) The genomic contents of the two copies of the 23S rRNA gene are different. In locus 1, the gene downstream of the 23S-5S gene is the gene encoding a von Willebrand/Integrin A Domain containing protein (VWA), while in locus 2, the 23S-5S gene is located in the complementary strand, and the downstream gene is the gene encoding YihY. The shaded region is the homologous region. hypo: hypothetical protein. (C) SNVs of 23S rRNA genes confirmed by colony PCR and Sanger sequencing. Individual colonies of H. pylori grown on plates were picked as the templates, and PCR of the 23S rRNA gene was performed. The amplified fragments were subjected to Sanger sequencing. There are both A and G fluorescence signals (green and black, respectively) at position 2143 of the 23S rRNA gene of strain Hpfe061.