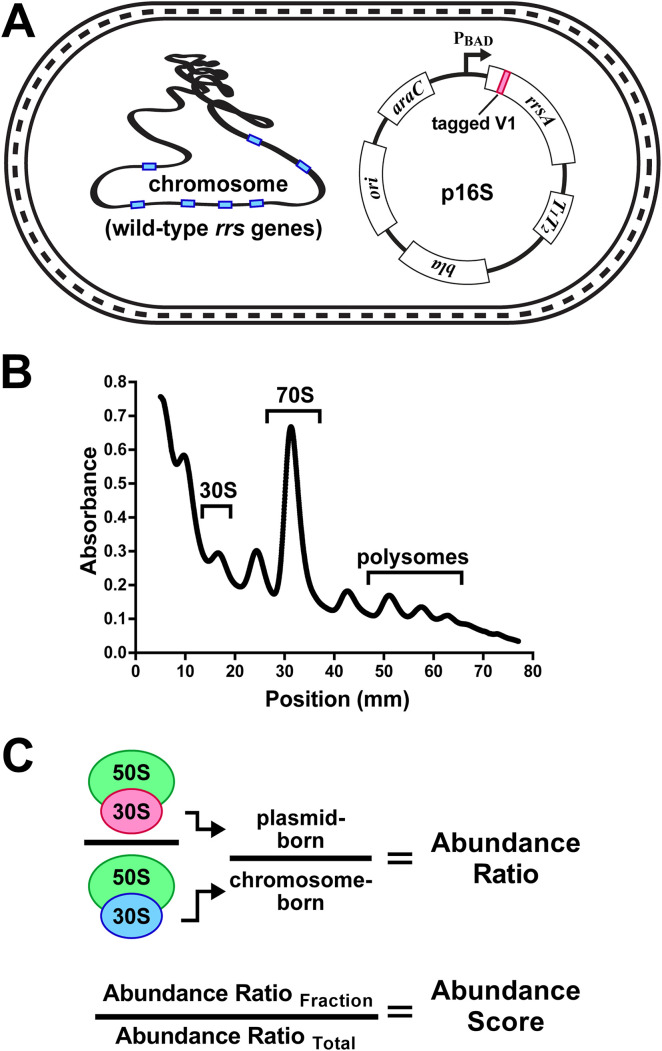
FIG 3.
Establishing the performance of 16S rRNA variants. Modified 16S rRNAs were evaluated in an E. coli strain with intact rrn operons. (A) The E. coli rrsA gene was cloned into a plasmid under the control of a tightly repressed PBAD promoter. The cloned rrsA was modified in its variable 1 (V1) region to contain a unique tracking tag sequence that was detectable using RT-qPCR. Other mutations were subsequently introduced in this tagged V1 rrsA for abundance evaluations of expressed 16S rRNA. (B) Fractionation of cell lysates using sucrose gradients allowed for isolation of 16S rRNAs in various stages of small subunit assembly and translation. The regions of 30S, 70S, and polysome material collected in this study are indicated. (C) RNA was extracted from gradient fractions and used to establish the abundance ratio of plasmid-born 16S relative to chromosome-born in the same fraction. An abundance score was then calculated by comparing the abundance ratio in a given fraction to that of the unfractionated lysate.