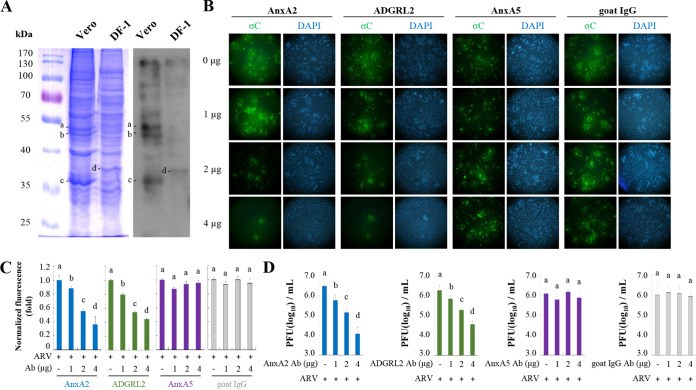
FIG 1.
Viral overlay protein-binding assay (VOPBA) analysis of avian reovirus (ARV) binding to Vero and DF-1 cell membrane proteins. (A) SDS-PAGE shows the Vero and DF-1 cell membrane proteins in the left panel. VOPBA was used to identify membrane proteins that bind to ARV as shown in the right panel. Binding of ARV to membrane proteins is shown at approximately 32 and 50 kDa, indicated by bands a, b, c, and d. Band a, ADGRL2; band b, AnxA5; bands c and d, AnxA2. These proteins were further identified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis. (B) Detection of internalized σC protein in ARV by antibody blocking assays. Confluent monolayers of Vero cells, grown in 8-well chambers for 24 h, were pre-incubated or not with anti-AnxA2, -AnxA5, and-ADGRL2 antibodies at the indicated concentrations for 1 h at 37°C. Goat-IgG was used as a negative control. After extensive washing, cells were incubated with ARV at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10 for 1 h, and the cells were fixed and stained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; blue) and antibodies specific for σC (green). (C) Fluorescence signals in panel B were quantified with ImageJ software. The amount of fluorescence in the mock control group was considered to be 1-fold. Duncan’s multiple range test (MDRT) using SPSS software was used to analyze the statistical significance of all data. (D) Virus yields were determined as treatments from panel B. Significance between treatments was determined by MDRT using SPSS software (version 20.0). Means with common lowercase letters (a, b, c, d) indicate no significant difference at P < 0.05. Each value is the mean (with standard error, SE) from three independent experiments.