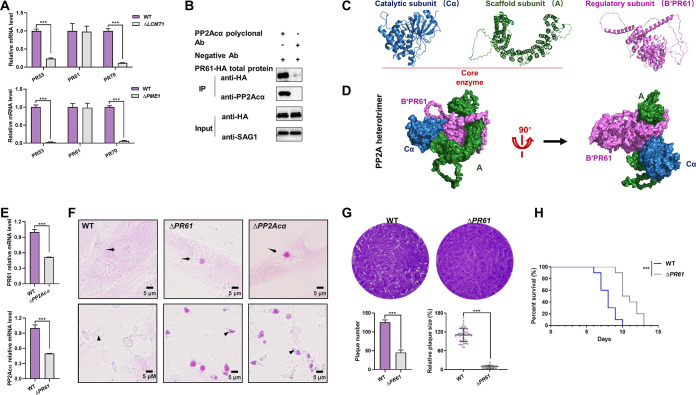
FIG 8.
B′/PR61 is the regulatory subunit of the PP2Acα holoenzyme that regulates glucose metabolism in tachyzoites. (A) Transcriptional levels of B′/PR53, B′/PR61, and B′′/PR70 in the wild-type (WT), leucine carboxyl methyl transferase 1 (LCMT1) knockout (ΔLCMT1), and protein phosphatase methylesterase 1 (PME1) knockout (ΔPME1) tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent repeats. ***, P ≤ 0.001, both by t tests. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of PP2Acα and HA-tagged B′/PR61. The cellular lysates of the tachyzoites (input) were incubated with protein A/G magnetic beads that had previously been incubated with PP2Acα polyclonal antibodies. Anti-HA/SAG1 antibodies are used in the Western blot analyses. (C) Three-dimensional models of PP2Acα, B′/PR61, and A subunits of T. gondii, as predicted by AlphaFold2. PP2Acα combines with one end of subunit A to form the core enzyme. (D) In silico-modeled PP2Acα-A-B′/PR61 heterotrimer of T. gondii, with the subunits indicated by blue, green, and pink, respectively. (E) Transcriptional levels of the B′/PR61 subunit in wild-type (WT) as well as PP2Acα knockout (ΔPP2Acα) tachyzoites, and vice versa. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent repeats. ***, P ≤ 0.001, both by t tests. (F) Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining. Wild-type (WT), B′/PR61 knockout (ΔPR61), and ΔPP2Acα tachyzoites within HFF-1 cells (top panels) and escaped from HFF-1 cells (bottom panels). Parasitophorous vacuoles and tachyzoites are indicated by black arrows and arrowheads, respectively. (G) The numbers and areas of the plaques formed by the WT and ΔPR61 tachyzoites. ***, P ≤ 0.001, by a t test. (H) Survival rate of ICR mice infected with WT and ΔPR61 tachyzoites, with 100 tachyzoites per mouse and 10 mice per group. ***, P ≤ 0.001.