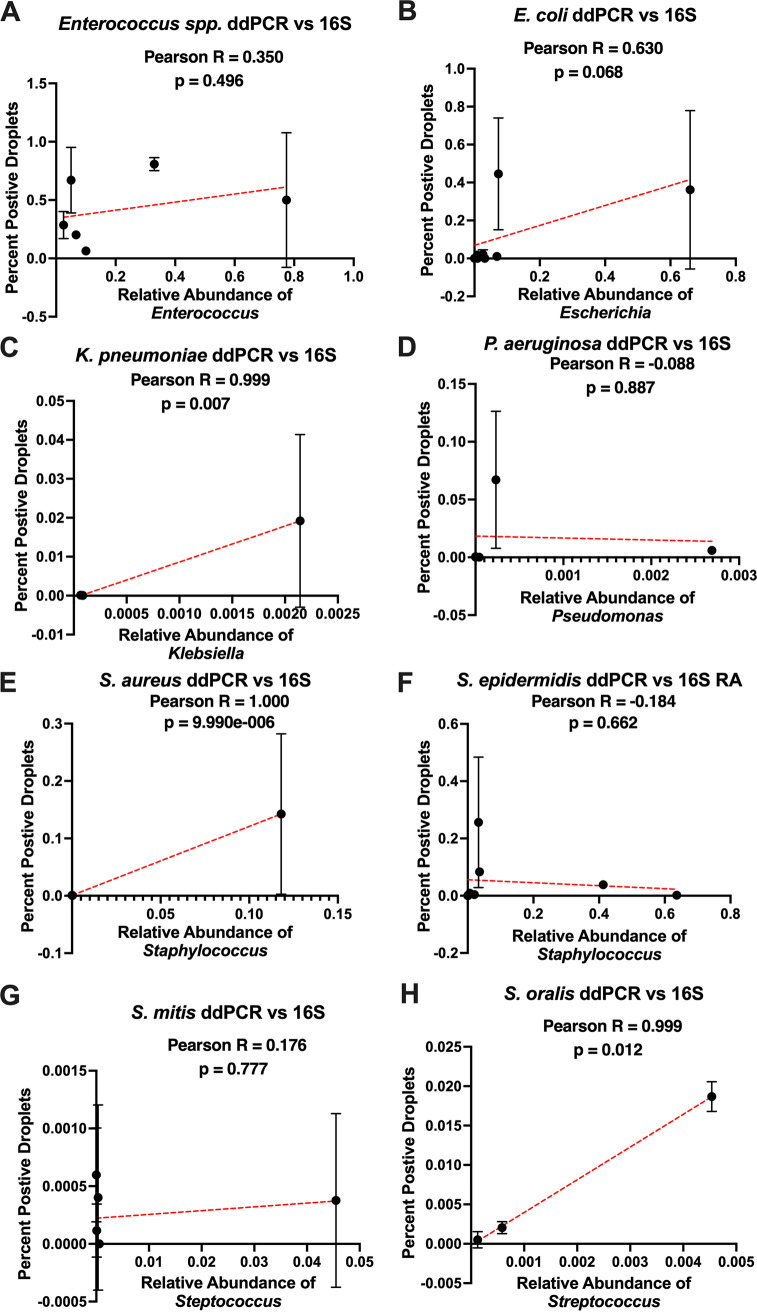
FIG 3.
Graphical depiction of percent positive droplets by ddPCR compared to relative abundance via 16S rRNA sequencing. Digital droplet PCR was performed on DNA extracted from stool samples of patients who were infected by Escherichia coli (A), Enterococcus spp. (B), Streptococcus mitis (C), Streptococcus oralis (D), Staphylococcus epidermidis (E), Klebsiella pneumoniae (F), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (G), and Staphylococcus aureus (H). ddPCR-positive percentages were determined by dividing the number of positive droplets by the total number of droplets. Those values were plotted against the relative abundance (RA) values gathered from 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The Pearson test was used to determine the correlation coefficient (r) and P values for all graphs. Simple linear regression was used to plot a line of best fit (red line) on each graph, where each dot represents an individual patient. A ROUT analysis was used to remove outliers from each data set prior to preforming the analysis.