Figure 1.
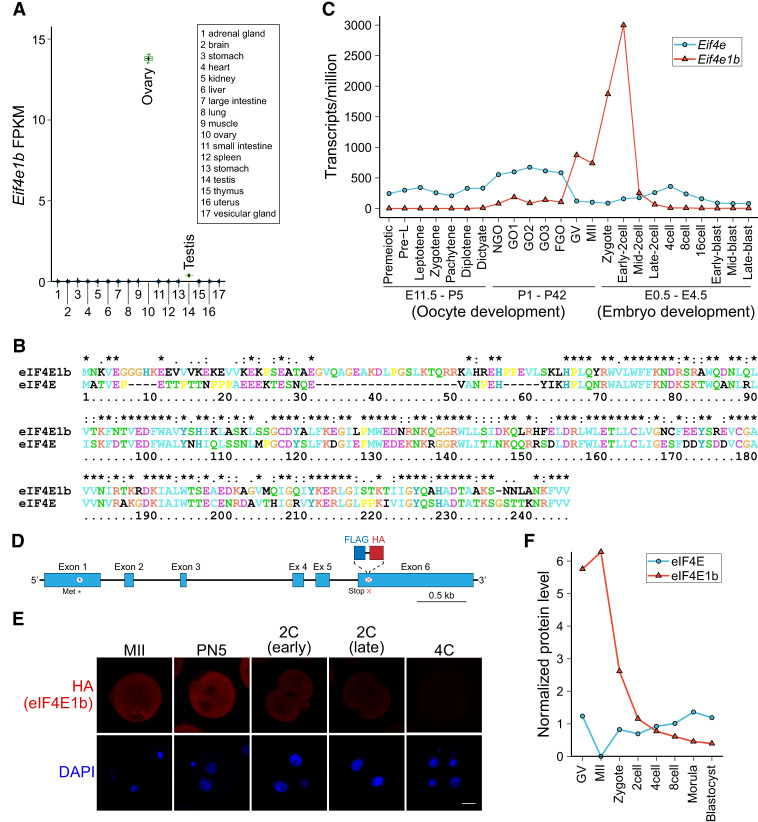
Eif4e1b expresses late in oogenesis and persists until two-cell embryos. (A) Abundance (FPKM [fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads]) of Eif4e1b transcripts in different tissues from published data. (B) Alignment of mouse eIF4E1b (NP_001028441.1) protein sequence with that of eIF4E (NP_031943.3). (C) Abundance (TPM [transcripts per million mapped reads]) of Eif4e1a (Eif4e) and Eif4e1b transcripts during mouse oogenesis and early embryo development. Eif4e1b transcripts are more abundant from GV to the early two-cell stage, while Eif4e is more abundant at other stages. (D) Schematic of the Eif4e1b gene locus in the Eif4e1bKI mouse line with FLAG and HA tags at the C terminus. (*) Initiator methionine, (x) stop codon. (E) Immunofluorescence of eggs and embryos derived from Eif4e1bKI female mice. Anti-HA antibody and DAPI were used to visualize the eIF4E1b fusion protein and nuclear DNA, respectively. Scale bar, 20 µm. (F) Protein levels of eIF4E and eIF4E1b from published proteomics results from GV oocyte to blastocyst stage.