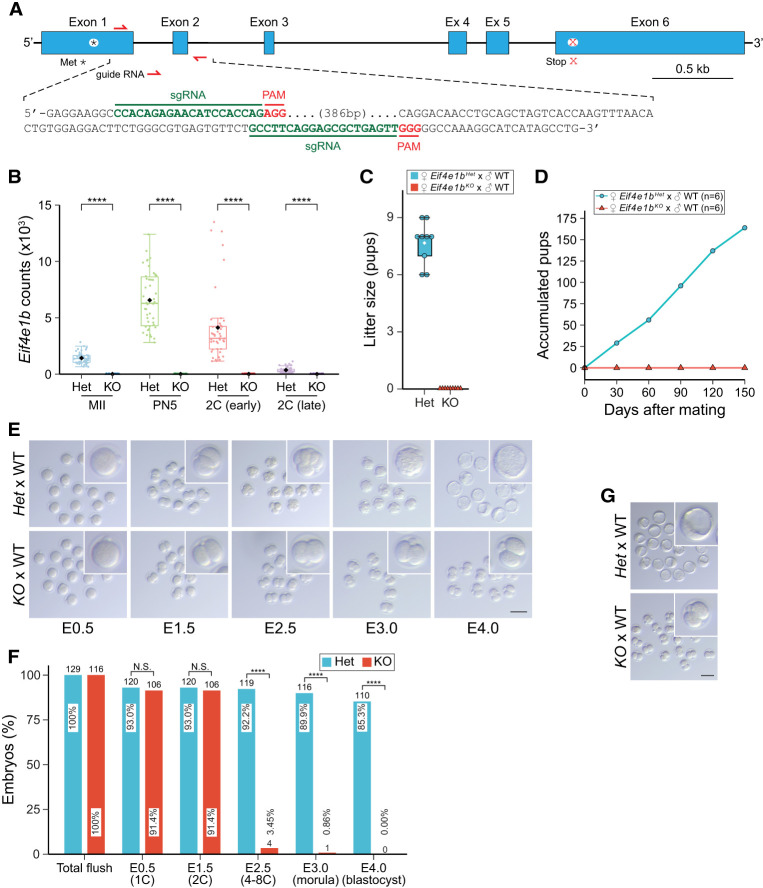
Figure 2.
Maternal deletion of Eif4e1b leads to developmental arrest at two cells. (A) Schematic of the Eif4e1b gene (top) and sequences of sgRNAs (bottom) for generation of Eif4e1bKO mouse lines. (*) Initiator methionine, (x) stop codon. (B) Abundance of read overlaps with Eif4e1b exon 1 or 2. Residual Eif4e1b transcripts in Eif4e1bKO female mice lack exons 1 and 2 and produce no functional eIF4E1b protein. (****) P < 0.0001; two-tailed t-test. (C) Six-week-old female Eif4e1bHet (control) and homozygous Eif4e1bKO mice were mated with WT males to determine litter sizes. (D). Accumulated pups from Eif4e1bHet and Eif4e1bKO females during 5 mo of continuous mating. (E) Representative images of in vitro cultured embryos from Eif4e1bHet and Eif4e1bKO females after mating with WT males at embryonic day 0.5 (E0.5), E1.5, E2.5, E3.0, and E4.0. Inset magnification, 2.5×. Scale bar, 100 µm. (F) Quantification of embryos in E. Ratio of embryos at different stages is plotted. Total number of embryos is above each bar. (N.S.) Not significant, (****) P < 0.0001; two-sided proportion test. (G) Images of embryos flushed from Eif4e1bHet and Eif4e1bKO female reproductive tracts at E3.5 after successful in vivo mating. Inset magnification, 2.5×. Scale bar, 100 µm.