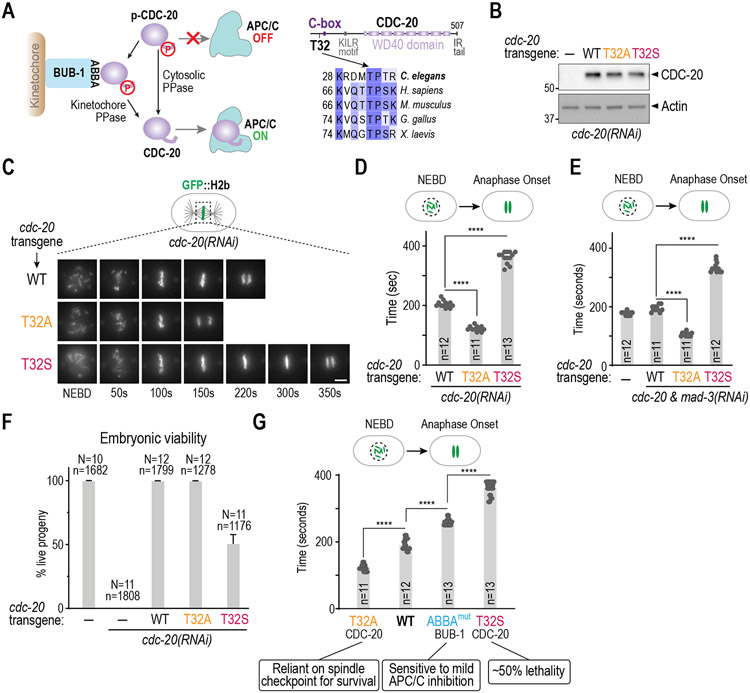
Figure 1. CDC-20 phosphoregulation controls early embryonic mitotic duration independently of the spindle checkpoint.
(A) (left) Schematic of APC/C control via CDC-20 phosphoregulation; (right) Sequence alignments highlighting the conserved Thr32 Cdk phosphosite. (B) Immunoblot of lysates from worms with the indicated RNAi-resistant cdc-20 mutant transgenes after depletion of endogenous CDC-20; actin serves as a loading control. (C) Stills from timelapse movies imaging chromosomes in embryos from the indicated conditions. Scale bar is 5 μm. (D) & (E) Quantification of the NEBD-anaphase onset interval for the indicated conditions. Bar height is the mean value. n is the number of embryos quantified. (F) Embryonic viability for the indicated conditions. N is number of worms whose progeny were scored and n is the number of embryos; mean and 95% confidence interval are plotted. (G) Relationship between mitotic duration and embryonic phenotypes. Phenotype annotations for T32A CDC-20 and ABBAmut BUB-1 are from previously published work 6. Data for CDC-20 T32A and T32S are the same as Figure 1D. All p-values are from unpaired t-tests; ****:p<0.0001. See Figure S1 for supporting information.