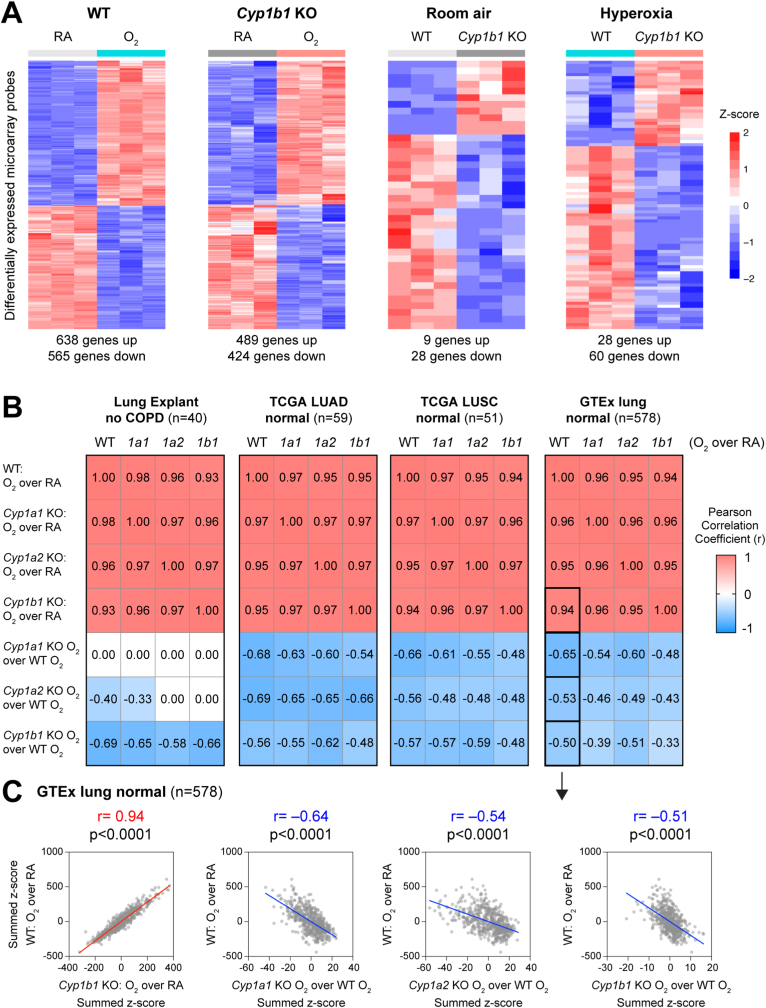
Fig. 2.
Cyp1b1-null mice exhibited a robust hyperoxia exposure response and potentially mitigated the wildtype response. A. Heatmaps of differentially expressed microarray probes, assessing hyperoxia response in WT or Cyp1b1-null mice (left) or differences between WT and Cyp1b1-null mice under either normoxia (RA) or hyperoxia (O2) conditions (right). The number of differentially expressed genes is listed below each heatmap (fold change exceeding 1.5X, FDR<0.05). B. Correlation of hyperoxia or mitigation gene signatures (as summed z-scores) using genes expressed in four cohorts of normal human lungs (GSE151052, TCGA LUAD, TCGA LUSC, GTEx lung). Pearson Correlation Coefficient was used, with significance achieved at p < 0.05. Black boxes indicate the four correlations shown as scatterplots in Panel C. C. Scatterplots indicating the correlation of the hyperoxia transcriptomic response in WT versus the hyperoxia response in the Cyp1b1-null mouse model, or versus the mitigation of the hyperoxia response by genetically modified mouse models Cyp1a1-null, Cyp1a2-null, or Cyp1b1-null. Axes show summed z-scores for the indicated comparison, with each point representing a patient sample from the GTEx human lung cohort.