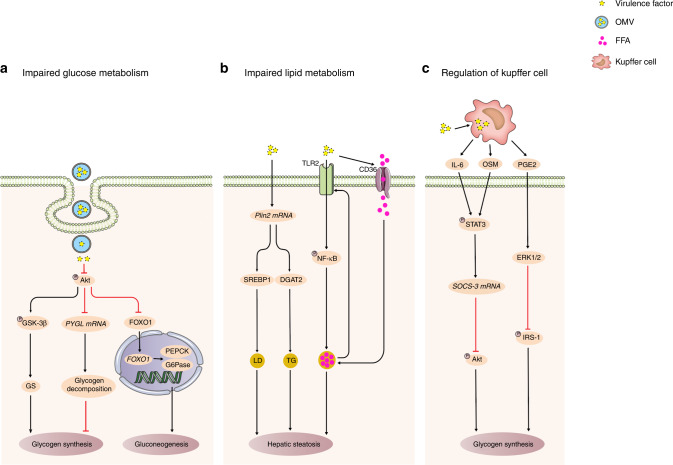
Fig. 4.
Mechanism underlying liver IR induced by periodontitis-derived virulence factors. a Impaired glucose metabolism. Virulence factors can result in abnormal glucose metabolism and participate in liver IR through decreased glycogen synthesis and increased gluconeogenesis. b Impaired lipid metabolism. Virulence factors can result in steatosis through ectopic deposition of FFAs, contributing to liver IR. c Regulation of Kupffer cell. Virulence factors can accumulate in Kupffer cells and activate them. Activated Kupffer cells can secrete IL-6, OSM and PGE2, leading to hepatocyte IR. Black arrows represent activating events; red arrows represent inhibitory events. Akt protein kinase B, GSK-3β glycogen synthase kinase-3β, GS glycogen synthase, PYGL glycogen phosphorylase L, FOXO1 forkhead box O1, PEPCK phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, G6Pase glucose 6-phosphatase, Plin2 perilipin 2, SREBP1 sterol-regulatory element-binding protein 1, LD lipid droplet, DGAT2 diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2, TG triglyceride, TLR2 Toll-like receptor 2, NF-κB nuclear factor κB, IL-6 interleukin-6, OSM tumor suppressor m, PGE2 prostaglandin E2, STAT3 signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, SOCS-3 suppressor of cytokine signaling-3, ERK extracellular regulated MAP kinase, IRS-1 insulin receptor substrate-1, OMV outer membrane vesicle, FFA free fatty acid