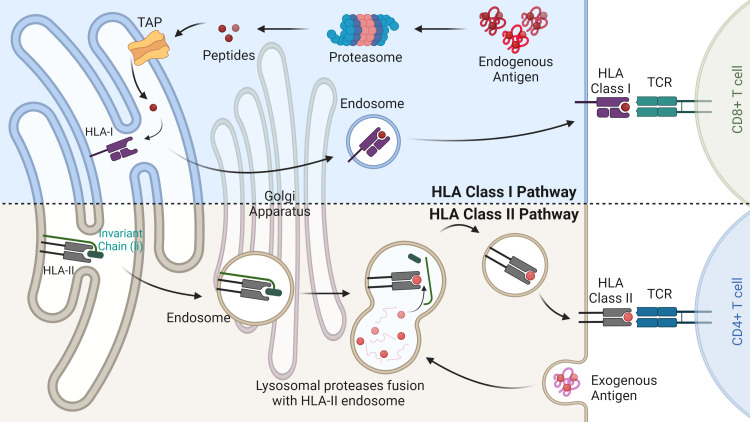
Figure 1.
HLA class I and II antigen-presentation pathways. The HLA class I pathway (above) is responsible for degrading endogenous antigens into peptides via the multi-catalytic proteasome complex. Peptides are then transported into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP). Here peptides bind based on their relative affinity to the allotypes present. HLA-I peptide complex is then transported through the Golgi apparatus to the cell surface where it is scrutinised by CD8+ T cells. The HLA class II pathway (below) involves the degradation of exogenous antigens in the endosome compartment. In the ER immature HLA-II proteins are stabilised by the invariant chain and released into the HLA class II compartment. Here, the enzyme HLA-DM removes the class II invariant chain peptide (CLIP) from the binding pocket allowing for antigenic peptide binding. Mature HLA-II molecules bound to their peptide cargo are then transported to the cell surface for CD4+ T cell recognition.