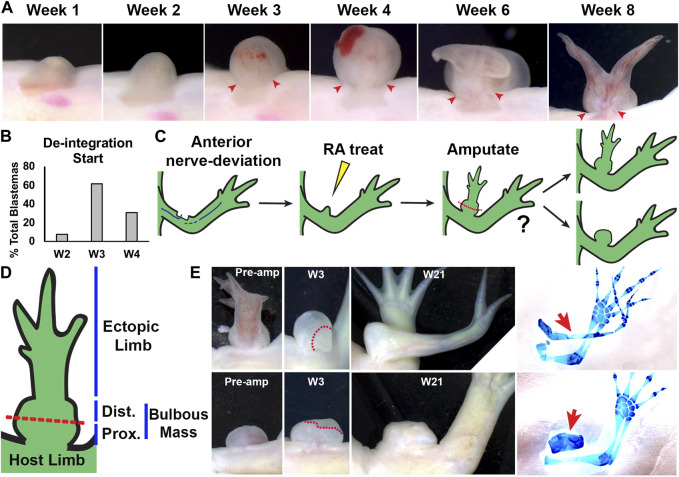
FIGURE 2.
Characterization of RA-induced ectopic tissue in innervated anterior wound sites: (A) Live image time course over 8 weeks of anterior-located blastemas treated with RA showing bulbous mass formation, and de-integration from the host limb. Red arrows mark the location where the bulbous mass is connected to the host limb at the time points when the bulbous mass is wider than the site of connection. (B) Histogram showing the time point when the RA treated blastemas (shown as % of the total blastemas) exhibited de-integration (N = 13) (C) Cartoon describing experiment design. Anterior located innervated limb wounds will generate blastemas, which upon systemic treatment with RA, will form ectopic structures connected to the host via bulbous mass tissue. Ectopic structures were amputated through the bulbous mass and were monitored for regeneration. (D) Diagram of RA-induced ectopic limb structure and bulbous mass. Red dotted line indicates the position of the amputation plane in the regeneration assay in (E). (E) Live images of RA-induced ectopic limb/bulbus mass (top) and RA-induced bulbous mass alone (lower) before amputation (Pre-amp), and 3 and 21 weeks (W3, W21) post-amputation. Dotted red line delineates the boundary between the remaining bulbous mass and the blastema. (right) The resulting ectopic structures are indicated with red arrows in the whole mount skeletal stained limbs. Table 2 has the full experimental statistics for (E).