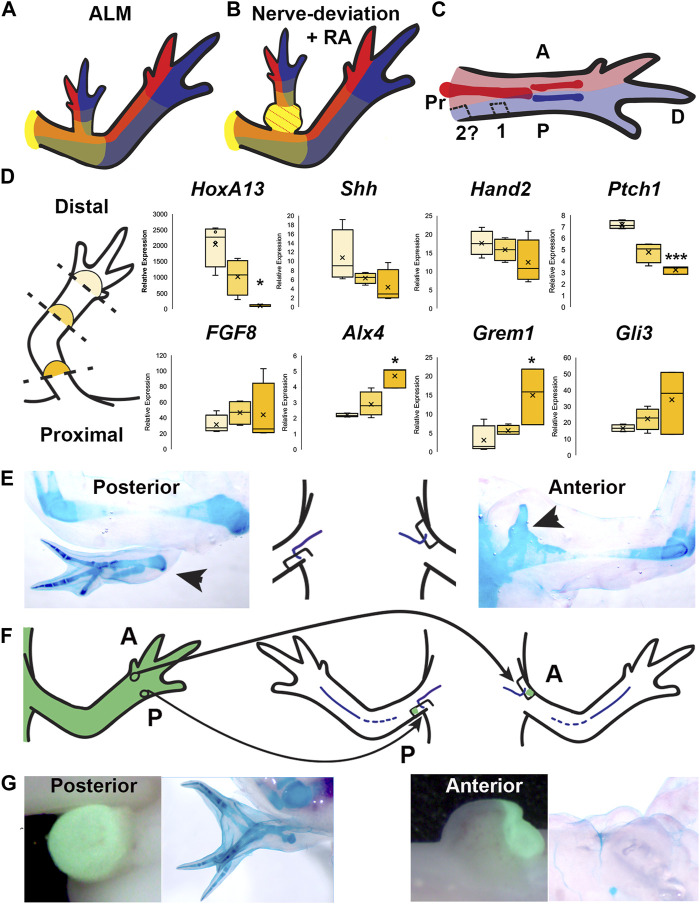
FIGURE 5.
Distribution of positional information in RA-induced ectopic limbs and normal limbs. (A, B) Cartoon representing the hypothesized distribution of anterior (red), posterior (blue), and the P/D (gradient of yellow, strongest in proximal) positional memory in ALM ectopic limbs (A) and RA-induced ectopic limbs with bulbus mass (B), and host limb tissues. Red dotted lines in bulbus mass indicate anterior positional information. (C) Cartoon representing the hypothesized distribution of A/P positional memories in the (internal) periskeletal tissue (dark red = anterior, dark blue = posterior) and (superficial) dermal tissue (light red and blue, respectively) in the uninjured limb. Squares indicate the hypothesized positional content in posterior ALM wound sites in mid-stylopod (1) and proximal stylopod (2) positions. (D) (left) Cartoon illustrating the localization of the blastemas collected for qRTPCR analysis. (right) Box and whisker plots of expressional data for HoxA13, Shh, Hand2, Ptch1, FGF8, Alx4, Grem1, and Gli3 from autopod (light yellow), stylopod (mid-tone yellow) and zeugopod (dark yellow) blastema samples. Statistical comparisons between the autopod and zeugopod or stylopod were performed using a two-tailed T-test with equal variance (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.005). All data represents the average of 4 biological replicates. (E) Cartoon illustrating the positioning of the nerve deviated wound sites on posterior and anterior limb base locations, flanked by images of whole mount skeletal preparations of the most extreme growth phenotypes in each position. (F) Cartoon illustrating the engraftment of distal anterior (A) and posterior (P) full-thickness skin into nerve-deviated wound sites at the limb base. (G) (Left) Live images of nerve deviated posterior and anterior wound sites at the limb base 3 weeks post-surgery where GFP + distal tissue graft is green. (Right) Whole mount (WM) skeletal preparation of wound sites 15 weeks post-surgery. Phenotype statistics of all surgical manipulations are provided in Table 4.