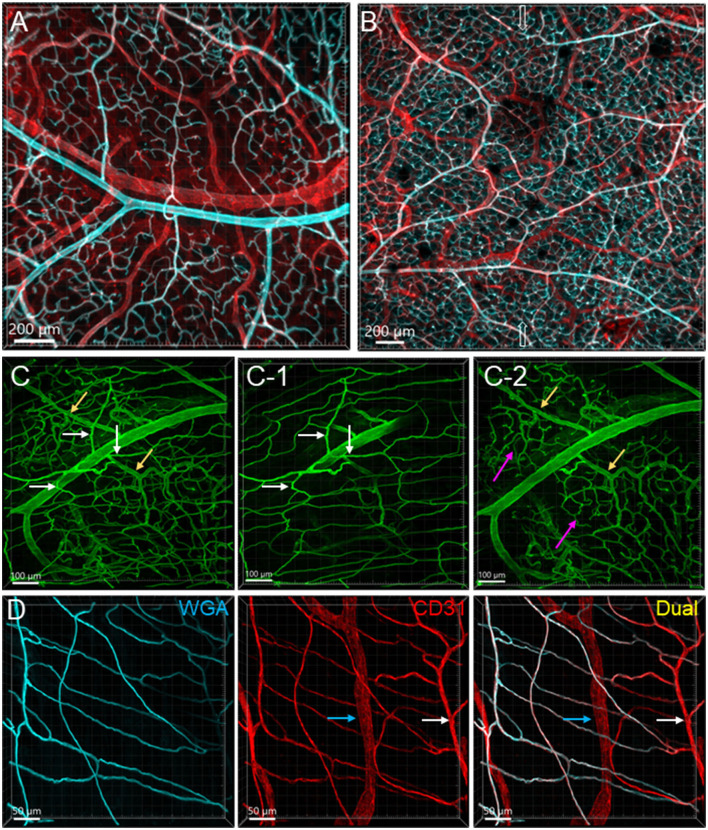
Figure 2.
Vascular branches and connections in the mouse colon. The vessels were labeled by WGA painting (cyan in A, B, D and green in C) and CD31 immunoreactivity (red). (A) Submucosal vessels ramified and lead to capillary webs at the base of mucosal crypts. The cyan and white-colored vessels are the arterial branches till capillaries and red colored ones are veins. The sample was collected from the aboral segment of a mouse mid-colon. (B) Microphotograph shows that in the submucosa vessels from each side of the colon wall are connected, and the microvessels anastomosed in the networks near the antimesenteric margin (indicated by empty arrows) in a sample from the distal colon. (C) Microphotographs demonstrate that arterioles from the same artery lead into capillary networks in the mucosa (yellow arrows) and muscle layers (white arrows). The muscle layers in (C-1) and mucosa in (C-2) were cropped images from (C). Magenta arrows indicate the capillary networks at the bottom of mucosal crypts. (D) Microvascular networks were labeled complementary by WGA and CD31 in muscle layers. White arrows indicate a CD31-labeled microvessel that was not perfused well by WGA. Blue arrows mark a lymphatic vessel labeled by CD31. The samples for images (C, D) were sampled from a mouse proximal colon.