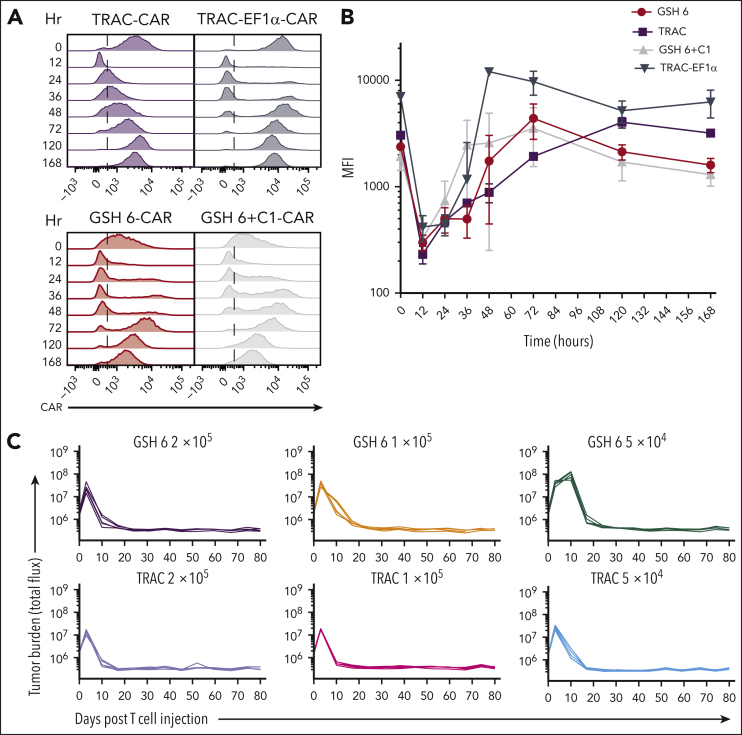
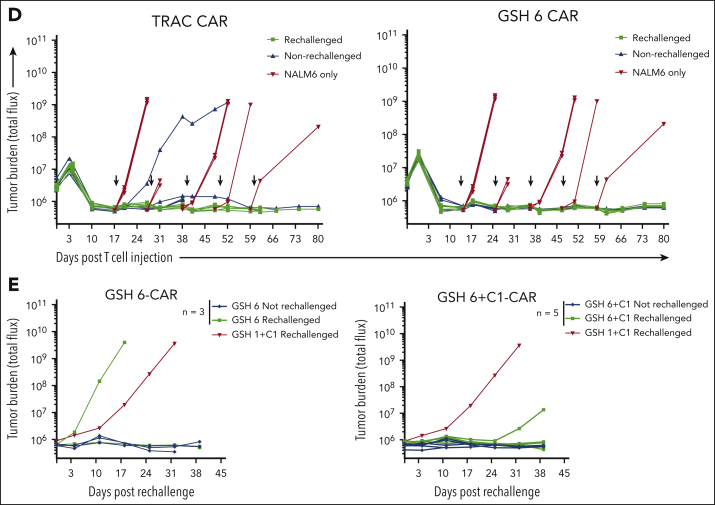
Figure 4.
GSH6 supports long-term tumor control at low T-cell doses and upon multiple rechallenges. (A) Representative flow plots depicting CAR expression on CAR+ T cells over a week after stimulation with CD19+ aAPCs in vitro. (B) Quantified median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CAR expression on CAR+ T cells shown in panel A (2 technical replicates each of 2 independent T-cell donors). Data are shown as mean ± SD. (C) Tumor burden in tumor bearing mice administered with GSH6-CARs without insulator C1 and TRAC-CARs at doses 2 × 105, 1 × 105, and 5 × 104 monitored over a period of 80 days after T-cell injection, n = 5. (D) Tumor burden of mice comparing the in vivo efficacy of GSH6-CAR and TRAC-CAR upon 5 tumor rechallenges 10 days apart starting at day 17 after T-cell injection vs no further rechallenge, followed for 80 days after CAR T-cell administration, n = 5 per group. The NALM6 only group represents treatment naïve, age-matched mice injected with NALM6 cells at the rechallenge timepoints (n = 2 mice each for the first 3 time points; n = 1 for the last 2 time points). (E) Tumor burden over 40 days after rechallenge with 1 × 106 NALM6 cells in mice surviving at day 100 after CAR T-cell administration (from Figure 3C). Some mice had to be euthanized or died of graft-vs-host disease, but none of them had tumor at the time of rechallenge.