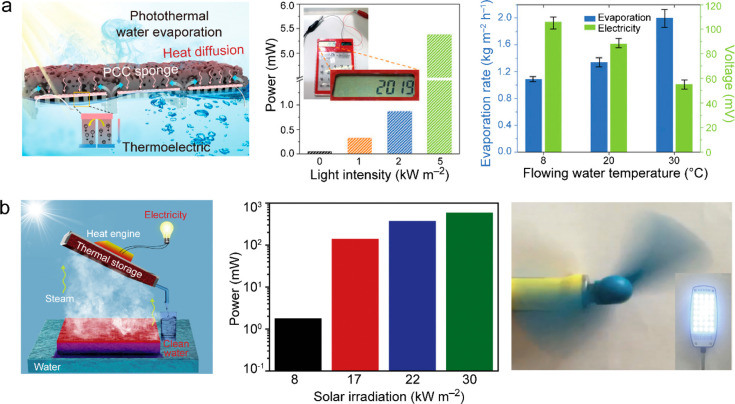
Figure 19.
Solar water heating for electricity generation. (a) Schematic of the interfacial photothermal water evaporation and electricity generation processes based on polydimethylsiloxane/carbon nanotubes/cellulose nanocrystals (PCC) sponge and thermoelectric modules (left panel). The middle panel shows the maximum output power of the thermoelectric modules under different solar irradiation powers with a digital calculator powered by the PCC sponge under 5 sun illumination shown in the inset. The right panel displays the water evaporation rates and open circuit voltages of the hybrid photothermal device at different flowing water temperatures under an optical density of 1 kW m–2. Reprinted with permission from ref (459). Copyright 2019 Wiley-VCH. (b) Schematic illustrating the condensation process during solar steam generation for the simultaneous generation of clean water and electricity (left panel). The middle panel shows the maximum output power of the thermoelectric device under different solar irradiation powers, and the right panel displays the optical image of an operating electric fan and light-emitting diodes powered by the solar steam system. Reprinted with permission from ref (461). Copyright 2018 under Elsevier user license.