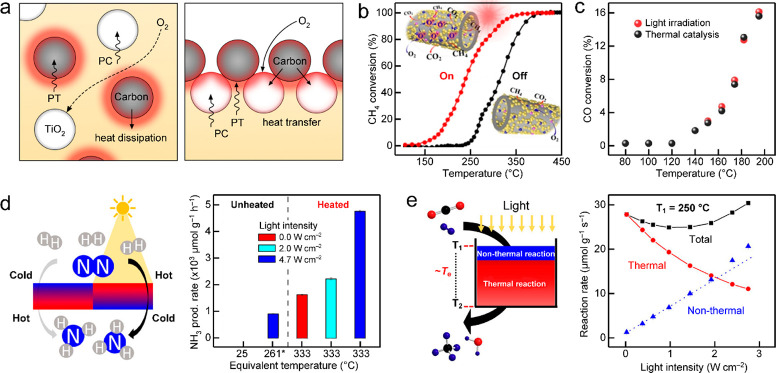
Figure 23.
Three categories of photothermal catalysis. (a) Thermally assisted photocatalysis. Schematic illustrating the photothermal effect and oxygen diffusion in a diphase (left) and a triphase (right) system. PC represents photocatalysis and PT represents the photothermal effect. Reprinted with permission from ref (276). Copyright 2021 Wiley-VCH. (b,c) Photoassisted thermocatalysis. The CH4 conversion with PdO/Mn3O4/CeO2 nanocomposite supported on 1D halloysite nanotubes with and without light irradiation (on and off) is shown in (b). Reprinted with permission from ref (635). Copyright 2021 Wiley-VCH. The CO conversion with a Co-based catalyst with and without UV–visible irradiation (photothermal heating/direct thermal heating) is shown in (c). Reprinted with permission from ref (636). Copyright 2018 Wiley-VCH. (d,e) Photothermal cocatalysis. The schematic (left) illustrating the effect of light-induced thermal gradients on ammonia production and the NH3 production rates (right) under dark and different illumination conditions are shown in (d). Reprinted with permission from ref (637). Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society. The schematic (left) showing the modified reaction chamber for the temperature measurements of thermal and nonthermal reactions and the total, thermal, and nonthermal reaction rates (right) as functions of the light intensity are shown in (e). Reprinted with permission from ref (639). Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.