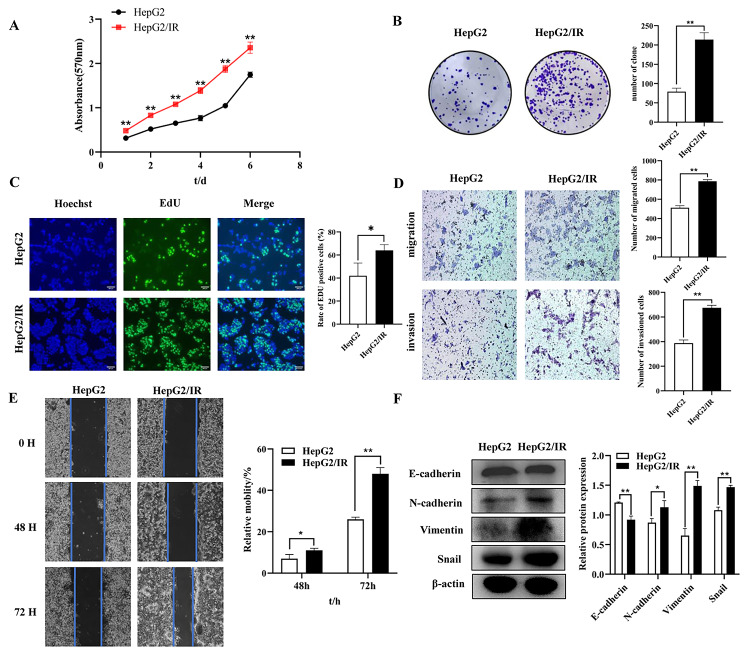
Fig. 1.
HepG2/IR cells displayed enhanced proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT. (A) MTT assays were performed with HepG2 and HepG2/IR cells. (B) Colony formation assays were performed with HepG2 and HepG2/IR cells. (C) DNA replication was detected by EdU assays in HepG2 and HepG2/IR cells. (D) Representative image of migration and invasion in HepG2 and HepG2/IR cells. (E) The migration of HepG2 and HepG2/IR cells was determined by scratch wound-healing assays. (F) The protein expression of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Vimentin and Snail in HepG2 and HepG2/IR cells was determined by Western blotting; the membranes were cut prior to hybridization with antibodies. The experiments were independently repeated three times. (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01)