Figure 5.
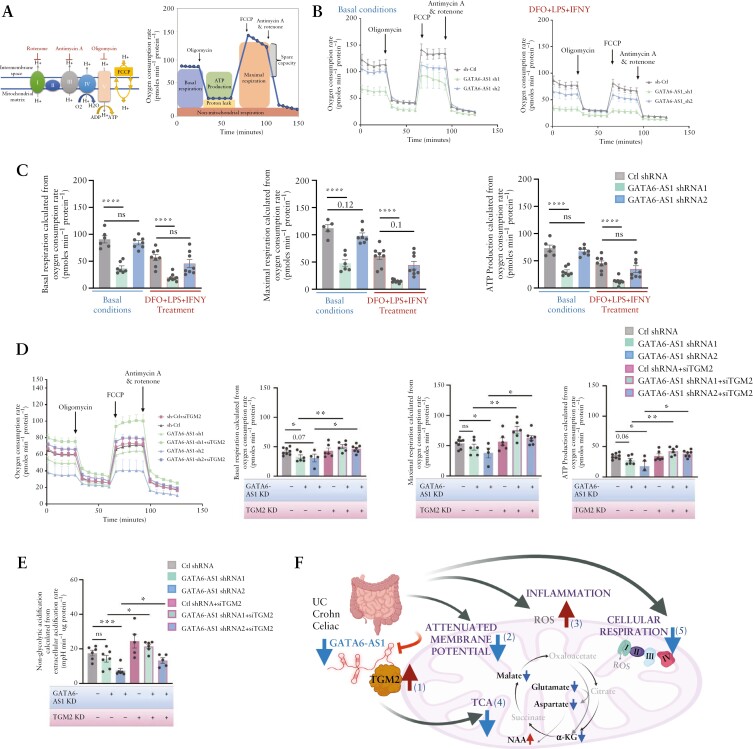
GATA6-AS1 silencing induces TGM2 expression and inhibits mitochondrial respiration while TGM2 co-silencing recovered mitochondrial respiration. [A] Schematic representation of the mitochondrial electron transport chain [I, II, III, IV] and ATP synthase [complex V], with the modulators included in the Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test. [B, C] Mito Stress Test measurement of oxygen consumption rate [OCR] in basal conditions and after sequential injections of oligomycin, FCCP and rotenone/antimycin A [B] in GATA6-AS1 knockdown and control Caco-2 cells without [left] and with [right] 100 µM DFO + 100 ng/ml LPS + 40 ng/ml IFNγ; changes in basal respiration, ATP production and maximal respiration were calculated [C]. [D] OCR [as in Figure 4B and C] in GATA6-AS1 knockdown and control cells transiently transfected with TGM2 or control siRNA to test whether reduction of TGM2 can rescue the GATA6-AS1 knockdown effect of cellular respiration. Changes in basal respiration, ATP production and maximal respiration. [E] Extracellular acidification rate [ECAR] was measured [see also Supplementary Figure S4]; non-glycolytic acidification was calculated and found to differ between GATA6-AS1 knockdown and control cells, and to be rescued by reduction of TGM2. Individual values are shown in the graph with their mean. All two-sided paired t-tests: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. [F] Concluding scheme; GATA6-AS1 is reduced in gut epithelia of UC, CD and coeliac cases, and mitochondrial function is impaired in epithelia of UC and CD patients.16,38,39 To model our observations in patients mechanistically, we showed that GATA6-AS1 binds a complex that includes TGM2 [1]. GATA6-AS1 silencing resulted in TGM2 induction, similarly to the induction seen in patients [1]. Reduction of GATA6-AS1 and TGM2 induction caused attenuation of mitochondrial membrane potential [2], higher production of mitochondrial ROS [3], reduction of TCA metabolites [4] and reduced cellular respiration [5]. Schemes were created with biorender.com.