Figure 7.
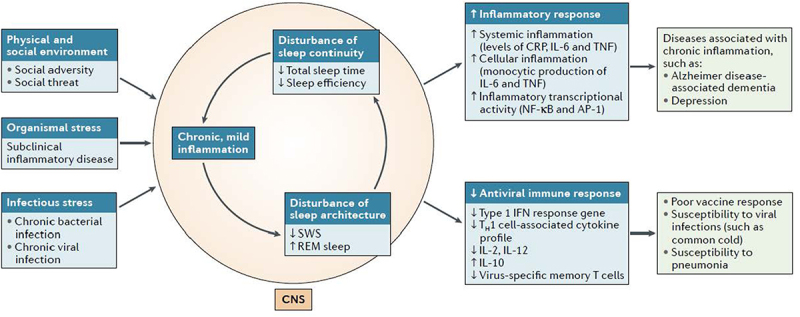
Model showing proposed links chronic perceived stress, organismal stress, or infectious stress and the induction of chronic, mild inflammation, which is associated with decreases in total sleep time, sleep efficiency and SWS, with increases in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Together these changes in sleep continuity and sleep architecture characterize sleep disturbance. Sleep disturbance, in turn, shifts the transcriptional profile toward increased inflammatory activity and decreased antiviral responses. The increase in the inflammatory transcriptional state is thought to contribute clinical manifestations of inflammatory disorders, whereas the decrease in antiviral responses is believed to result in poor vaccine responses and increased susceptibility to infectious disease.
AP-1, activator protein 1; CNS, central nervous system; CRP, C- reactive protein; NF- κB, nuclear factor- κB; TH1 cell, T helper 1 cell; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.As reprinted from Irwin [27] with permission.
