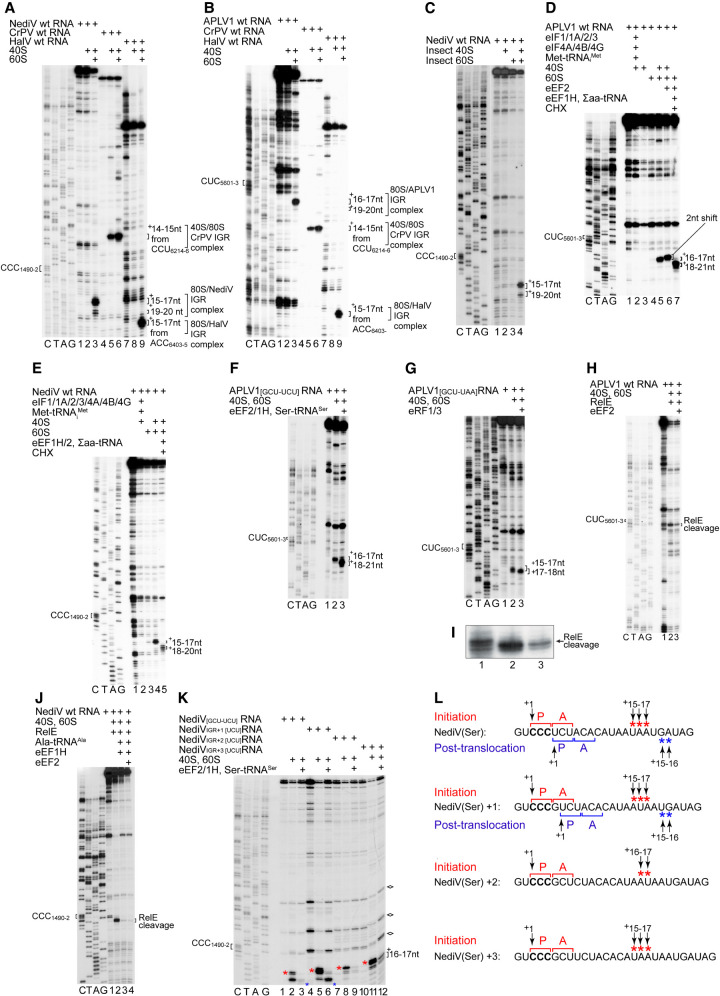
FIGURE 3.
The mechanism of initiation on type 6d IRESs. (A,B) Assembly of ribosomes from 40S and 60S subunits on (A) NediV, (B) APLV1 and (A,B) CrPV and HalV IRESs, assayed by toeprinting. The NediV CCC1490–2 and APLV1 CUC5601–3 triplets that precede ORF2 are indicated on the left and the positions of toeprints relative to these codons are indicated on the right of panels A–K. (A) The +15–17 nt toeprints on the right correspond to binding of NediV CCC1490–2 in the P site of IRES-bound ribosomes; the +19–20 toeprints are discussed in the text. (B) The +16–17 nt toeprints on the right correspond to binding of APLV1 CUC5601–3 in the P site of IRES-bound ribosomes, analogously to the toeprints +14–15 nt from CrPV CCU6214–6 and +15–17 nt from HalV ACC6403–5. (C) Assembly of S. frugiperda ribosomes on the NediV IRES, assayed by toeprinting. (D–F) Toeprinting analysis of ribosome assembly and subsequent elongation on (D) APLV1 wt, (E) NediV wt, and (F) APLV1[GCU-UCU] mutant mRNAs incubated with ribosomal subunits with (D,E) or without (F) canonical eIFs and Met-tRNAMeti and with (D,E) eEF1H/2, ∑aa-tRNA and cycloheximide (CHX) or (F) eEF1H/2 and Ser-tRNASer. The shifts in toeprints (D) caused by eEF2 alone and (D–F) after the first cycle of elongation are indicated on the right of each panel. (G) A-site accessibility in 80S:IRES binary complexes analyzed by binding eRF1/eRF3 and eEF2 to APLV1[GCU-UAA] mRNA, assayed by toeprinting. The positions of toeprints relative to the P site codon CUC5601–3 are indicated on the right. (H–J) A-site accessibility in 80S complexes assembled on (H,I) APLV1 and (J) NediV IRESs, assayed by RelE cleavage. RelE cleavage of the APLV1 IRES in (H) is shown at high resolution in (I). Sites of cleavage are indicated on the right. (K,L) The fidelity of reading frame selection investigated by the ability of 80S complexes formed on the NediV IRES with (K) a UCU (Ser) codon in the 0 reading frame or placed in the +1, +2, or +3 reading frames by inserting G, GC, and GCT nucleotides, respectively, between CCC1490–1492 and UCU1493–1495 (Ser) codons to undergo a single cycle of elongation in presence of Ser-tRNASer, eEF1H/2, and ribosomal subunits, assayed by toeprinting. Stops induced by initiation and post-translocation 80S ribosomes are indicated by red and blue asterisks, respectively. RT stops induced by structured RNA elements independently of ribosomes are marked with diamonds on the right. (L) The initiation codon (bold) and flanking nucleotide sequences of NediV[UCU], NediVIGR + 1[UCU], NediVIGR + 2[UCU] and NediVIGR + 3[UCU] mRNAs annotated to show the P site and A site codons in 80S initiation and post-translocation complexes above and below individual mRNA sequences, together with the +1 nt in the P site of pretranslocation complexes, and the toeprints from 80S initiation and post-translocation complexes (red and blue asterisks, as in panel K above and below individual mRNA sequences). Panel L summarizes data from panel K. (A–K) Lanes C, T, A, G show dideoxynucleotide sequence of (A,C,E,I,J,K) NediV and (B,D,F,G,H) APLV1 mRNAs generated with the same primer as in toeprinting assays. Positions of P sites (CCC1490–2 and CUC5601–3 for NediV and APLV1, respectively) and 80S:IRES complexes are indicated. (C,D) Separation of lanes by white lines indicates that they were juxtaposed from the same gel.